
Startups Are Inventing Cooling Clothes for a Hotter Future
Every morning, thousands of construction workers in Qatar start their day by soaking their uniforms in water. The
2023-09-01 18:45

Scientists may have just found a cure for alcoholism
Alcohol addiction ruins millions of lives every year, but scientists may have found a cure for this terrible affliction. A new treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD) has been trialled in monkeys with impressive results and, if these translate to human trials, the impact could be monumental. A team of neuroscientists and physiologists from across the US tested a new type of gene therapy to see if they could directly target the underlying brain circuitry associated with sustained heavy drinking. As they noted, in the journal Nature Medicine, people suffering from AUD commonly return to alcohol use even if they attempt to quit. This is largely to do with what’s known as mesolimbic dopamine (DA) signalling – meaning how the central nervous system circuit communicates the feelgood neurotransmitter dopamine. A protein called glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is key to keeping these neurons in this reward circuitry functioning. However, experts have found that levels of GDNF are reduced in people with AUD during periods of alcohol abstinence, most notably in a region of the brain called the ventral tegmental area (VTA), as IFLScience notes. Therefore, the researchers decided to test whether using gene therapy to deliver more GDNF to the VTA could help reinforce this crucial dopaminergic signalling and prevent patients from suffering an alcoholic relapse. The team of scientists explained how alcohol consumption in non-addicts prompts the release of dopamine, creating a pleasurable buzz feeling, but chronic alcohol use causes the brain to adapt and stop releasing so much dopamine. “So when people are addicted to alcohol, they don’t really feel more pleasure in drinking,” Dr Kathleen Grant, a senior co-author of the study, said in a statement. “It seems that they’re drinking more because they feel a need to maintain an intoxicated state.” For their research, Dr Grant and her colleagues used eight rhesus macaque monkeys, who were exposed to increasing concentrations of alcohol over four 30-day “induction” periods. The monkeys then had free access to alcohol and water for 21 hours a day for six months, during which they developed heavy drinking behaviours. This was then followed by a 12-week abstinence phase, with the GDNF treatment performed four weeks in for half of the subjects. The gene therapy was delivered using a a viral vector containing a copy of the human GDNF gene injected directly into the primate’s VTA, according to IFLScience. And the results were truly jaw-dropping. “Drinking went down to almost zero,” Dr Grant said. “For months on end, these animals would choose to drink water and just avoid drinking alcohol altogether. They decreased their drinking to the point that it was so low we didn’t record a blood-alcohol level.” The most exciting aspect of their findings is the suggestion that gene therapy could offer a permanent solution for people with the most severe cases of AUD. This will be a welcome glimmer of hope to many, given that some 29.5 million people were diagnosed with AUD in the US alone in 2021, according to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Of these 29.5 million sufferers, almost a million (894,000) were aged between 12 and 17. It’ll likely be some time before we know for sure whether the gene therapy can be rolled out in humans, but it’s an important first step in tackling this devastating disorder. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 19:54

A dead vampire star is firing out 'cosmic cannonballs'
A dead “vampire” star is feeding on a nearby companion and expelling cannonballs and its behaviour has left astronomers stunned. The dead star is located around 4,500 light-years away and, until now, has baffled astronomers with its unusual behaviour. It is a rapidly spinning neutron star, otherwise known as a pulsar, that has been given the name PSR J1023+0038, shortened to J1023. It emits radiation from both its poles that occasionally reach Earth and also appears to have two different “settings” of brightness. Initially, the behaviour of J1023 confused experts, but now they believe that the stark difference in brightness levels has to do with the star launching out matter over short spaces of time. Maria Cristina Baglio, leader of the research team and scientist at New York University, Abu Dhabi, said in a statement: “We have witnessed extraordinary cosmic events where enormous amounts of matter, similar to cosmic cannonballs, are launched into space within a very brief time span of tens of seconds from a small, dense celestial object rotating at incredibly high speeds.” In addition to the pulsar emitting matter, over the last 10 years, scientists have witnessed the star pulling material from its companion star. The material it is stealing forms a structure called an accretion disk that forms around the star itself. Since it began feeding, the star has been alternating between between “low” and “high” power modes. During moments of high power, the star shines brightly with a variation of X-rays, ultraviolet and visible light. During low power, it emits radio waves and appears much dimmer. In June 2021, experts witnessed a star shooting out hot, luminous matter that has been compared to a cosmic cannonball as the star continually switched modes. J1023 has fascinated experts, who have been able to explain the way the star behaves by observing it. Despite solving many of its mysteries, the scientists aren’t done with it yet. With the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) in northern Chile currently under construction, it is hoped that when it is ready, scientists will once more be able to observe the pulsar. Sergio Campana, research co-author and Research Director at the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics Brera Observatory, said: “The ELT will allow us to gain key insights into how the abundance, distribution, dynamics and energetics of the inflowing matter around the pulsar are affected by the mode switching behavior.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 17:27
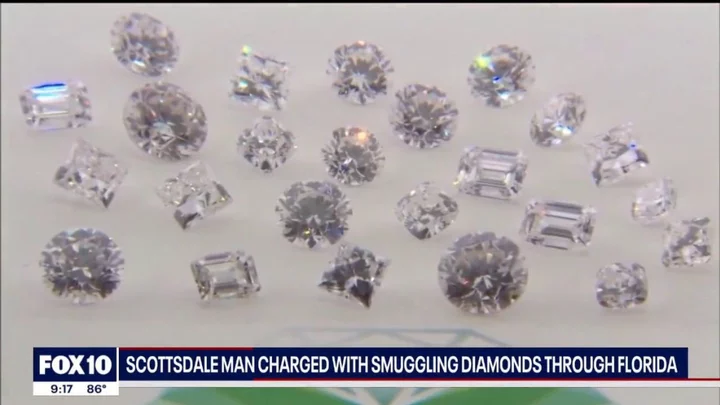
Geologists have figured out how to locate diamond ‘explosions’
A group of geologists has recently achieved a breakthrough in identifying potential sites for the formation of diamonds. Diamonds, the hardest naturally occurring material we have found, originate under the extreme conditions of immense pressure and high temperatures deep within the Earth's interior. These precious gems are occasionally pushed to the surface in molten rock formations known as kimberlite. However, there are currently two competing theories regarding what is responsible for this rush of kimberlite which brings diamonds to the surface. In a recent study, these theories were closely examined by a research team. In a piece for The Conversation study author and Associate Professor in Earth Science at the University of Southampton, Thomas Gernon explained: “one proposes that kimberlite magmas exploit the ‘wounds’ created when the Earth’s crust is stretched or when the slabs of solid rock covering the Earth - known as tectonic plates - split up.” “The other theory involves mantle plumes, colossal upwellings of molten rock from the core-mantle boundary, located about 2,900km [1,802] beneath the Earth’s surface.” However, neither of these theories adequately explains how magma manages to find its way through the Earth's crust, or the specific composition of the resulting kimberlite. By employing statistical analysis and machine learning, the team analysed the breakup of continents and its correlation with kimberlite formation. Their findings indicated that the majority of kimberlite volcanoes erupt 20 to 30 million years after tectonic breakup. “It also added a major clue,” Gernon explained. “Kimberlite eruptions tend to gradually migrate from the continental edges to the interiors over time at a rate that is uniform across the continents.” Delving deeper into their investigation through computer-generated models, the team ultimately concluded that diamond eruptions stem from a "domino effect." As continents gradually drift apart from each other, they generate rifts of thinned crust. As this happens, regions of thick, cold rock descend into the hot magma beneath, inducing an upsurge of the mantle, which in turn triggers a similar flow in nearby continents. Gernon elaborated on the team's findings, saying, "Various other results from our computer models then advance to show that this process can bring together the necessary ingredients in the right amounts to trigger just enough melting to generate gas-rich kimberlites,” Gernon explained. “Once formed, and with great buoyancy provided by carbon dioxide and water, the magma can rise rapidly to the surface carrying its precious cargo.” Moreover, the same methodology could potentially be employed to locate diamonds and other rare elements. “The processes triggering the eruptions that bring diamonds to the surface appear to be highly systematic,” Gernon siad. “They start on the edges of continents and migrate towards the interior at a relatively uniform rate.” The study is published in the journal Nature. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 00:18

Doctor says scientists secretly made a ‘humanzee’ by mixing humans with chimps
Chimpanzees are our closest relatives, so it’s not surprising that they can do many of the things that we can. They’re able to create tools and can even use sign language, plus they share 98.8 per cent of their DNA with humans. It is, therefore, no wonder that the question has often been asked: could humans and chimps ever produce offspring? The answer, according to one evolutionary psychologist, is yes – and it’s already happened. Gordum Gallup made the eyebrow-raising claims in an interview with The Sun Online back in 2018. He told the news site that a human-chimpanzee hybrid – which he dubbed a “humanzee” – was born in a Florida lab 100 years ago. And if you’re wondering how the scientists behind the experiment managed to keep it hushed up for decades, it’s because – according to Gallup – they swiftly killed the infant when they realised the implications of what they’d done. Gallup, a professor at New York’s University at Albany, said his former university teacher told him that the secret birth took place at a research facility in Orange Park, where he used to work. “They inseminated a female chimpanzee with human semen from an undisclosed donor and claimed not only that pregnancy occurred but the pregnancy went full term and resulted in a live birth,” the psychologist told The Sun. “But in a matter of days, or a few weeks, they began to consider the moral and ethical considerations and the infant was euthanised.” Putting Gallup’s unsubstantiated story to one side, it’s unclear whether a human-chimpanzee hybrid is even possible. Some experts believe that our human ancestors and chimpanzees may have been capable of interbreeding as late as 4 million years ago according to IFL Science, which notes that our last common ancestor lived 6-7 million years ago. However, the website also notes that this theory is widely contested. It also points out that other animals with similar genetic differences to that of humans and chimps, such as horses and zebras, have been able to reproduce. And yet, the offspring are often infertile. Nevertheless, back in the 1970s, plenty of people believed that a chimp called Oliver was a human-monkey hybrid thanks to his humanistic walk, intelligence and physical features (he was said to have a smaller, flatter face than his ape peers, according to Historic Mysteries). It wasn't until tests were conducted on Oliver in 1996 that the matter was finally settled: he had 48 chromosomes so was categorically not a humanzee but a regular chimp. Oliver The Humanzee www.youtube.com Still, one certainty is that scientists continue to tread an ethical tightrope when it comes to investigating chimps and their potential to further biomedical research. In 2021, scientists created the first (publicly documented) part-monkey, part-human embryo by growing human stem cells in a macaque monkey. The aim of the work, which was carried out at California’s Salk Institute, was to help create organs for transplants and improve our understanding of human development and disease progression. In 2020, a team of German and Japanese scientists spliced human genes into the brains of marmosets, resulting in the monkey fetuses having larger, more human-like brains, according to the study, which was published in the journal Science. Once the experiment was complete, the team destroyed their creations “in light of potentially unforeseeable consequences with regard to postnatal brain function”. One thing’s for sure, no scientist wants to find themselves the architect of a real-life Planet of the Apes. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-31 00:17
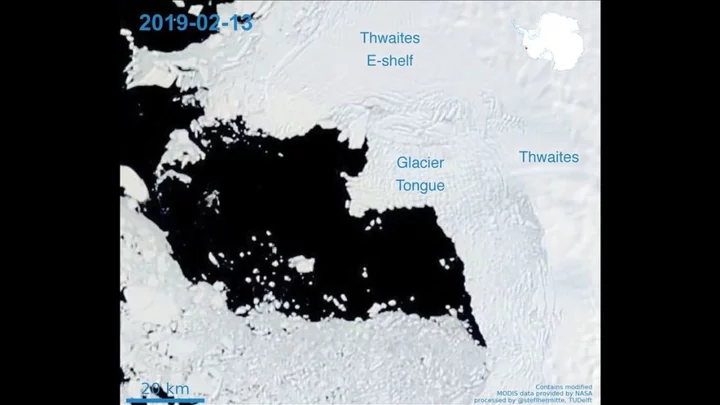
Scientists troubled by 'doomsday glacier' discovery
Scientists have been left shocked and worried by a recent discovery made beneath the Thwaites Glacier in Antarctica, otherwise known as the 'doomsday glacier.' The huge amount of ice has been destablised and has been reduced by nearly nine miles since the 1990s. It is believed to hold a large amount of water, that if it were to completely melt would raise sea levels by more than 2 feet around the globe and could unleash more water if neighbouring glaciers are disturbed. Now, new research carried out at the location in West Antarctica that deeper cracks are beginning to form on the shelf of the glacier potentially compromising its intergrity, as published in a study on the science journal Nature. Scientists used a robot named 'Icefin' to bore 2000 ft down below the glacier's surface to get a better look at what is going on beneath it by taking photos and videos as well as collecting valuable pieces of data about temperature and sea levels. What they found wasn't very reassuring. Although the rate of the melting wasn't as fast as they had originally feared the researched still painted a "very nuanced and complex picture." Speaking to CNN, lead researcher Peter Davis said: "The glacier is still in trouble. What we have found is that despite small amounts of melting there is still rapid glacier retreat, so it seems that it doesn’t take a lot to push the glacier out of balance." However, it wasn't all doom and gloom as robot creator and scientist Britney Schmidt of Cornell University, revealed that signs of life had been found on the glacier. She said: "To accidentally find them here in this environment was really, really cool. We were so tired that you kind of wonder like, ‘am I really seeing what I’m seeing?'. "You know because there are these little creepy alien guys (the anemones) hanging out on the ice-ocean interface. In the background is like all these sparkling stars that are like rocks and sediment and things that were picked up from the glacier. And then the anemones. It’s really kind of a wild experience." That being said, Oregon State University ice researcher Erin Pettit, who didn't work on the study believes that the findings are a cause for concern. She told Associated Press: "Thwaites is a rapidly changing system, much more rapidly changing than when we started this work five years ago and even since we were in the field three years ago. I am definitely expecting the rapid change to continue and accelerate over the next few years." Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-30 23:29
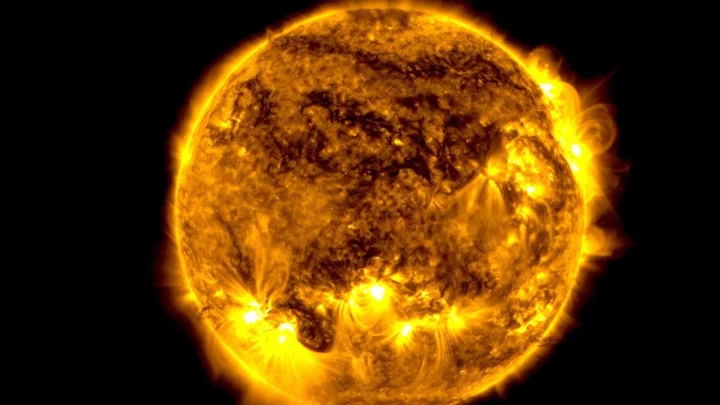

Part of the sun is broken and scientists are baffled
We don’t want to alarm anyone, but the sun is broken. A section of the sun has left the surface and begun circulating around the top of the star as if it were a huge polar vortex, and it’s not exactly clear why it’s happened. The observation was made possible thanks to the James Webb Space Telescope, and its no surprise that it piqued the interests of scientists everywhere. Tamitha Skov is a space weather physicist who regularly shares updates on social media, and she seemed incredibly excited about the latest developments. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter “Talk about Polar Vortex! Material from a northern prominence just broke away from the main filament & is now circulating in a massive polar vortex around the north pole of our Star,” she wrote. “Implications for understanding the Sun's atmospheric dynamics above 55° here cannot be overstated!” Solar prominences consist of hydrogen and helium, and they extrude from the sun’s service releasing plasma. While there’s confusion around the cause of the phenomenon, it could be related to the reversal of the sun’s magnetic field, as well as the fact that something expected has been known to happen when the sun reaches a 55 degree latitude in every 11-year solar cycle. Solar physicist Scott McIntosh, who is the deputy director at the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colorado told Space.com: "Once every solar cycle, it forms at the 55 degree latitude and it starts to march up to the solar poles. “It's very curious. There is a big 'why' question around it. Why does it only move toward the pole one time and then disappears and then comes back, magically, three or four years later in exactly the same region?" Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-30 22:47

Scientists think there might be life hidden in underground caves on Mars
Scientists have theorised that if we are going to find life on Mars, it will be microbes and they will be living in caves below the surface. The Perseverance rover, NASA’s exploration robot on the Red Planet, is currently searching for signs of ancient life in the Jezero Crater. Scientists already know that there are so-called lava tubes on Mars, which some think could be large enough to shelter the first human astronauts from the cosmic radiation which is bombarding the planet. When these were formed, they thought conditions on Mars were more similar to those on Earth, with flowing water, an atmosphere and a warmer climate. One theory is that as conditions changed on the surface and Mars lost its magnetic field and atmosphere, life could have shifted underground. Daniel Viúdez-Moreiras from Spain’s National Institute for Aerospace Technology calculated that UV radiation levels would be about 2 percent of the radiation levels found at the surface. Fortunately, we have lava tubes here on Earth too, which could tell us what life could look like in similar conditions elsewhere in the Solar System. Hawai’i’s Mauna Loa volcano lava tubes were recently explored by NASA. Within them, life is sheltered from conditions on the surface. On Earth, that is a bad thing: we have sunlight and oxygen. But on Mars, where conditions are much harsher, that is a big advantage. “The microbes we found in Hawaii could be similar to microbes that once lived on Mars,” researcher Chloe Fishman explained to NASA following a trip to collect samples in April, “or even microbes that live there today.” The team brought back samples from the cave so as to sequence the genomes of the microbes they found there. And there are already plans to explore lava tubes on the Moon, too. So maybe, just maybe, they will hold the secret to life on Mars. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-30 19:55

CNN Reportedly Poised to Pick Mark Thompson as Next CEO
Mark Thompson, the former chief executive officer of The New York Times Co., is set to take up
2023-08-30 10:51
More than 1 billion people worldwide are infected with parasitic worms
After a live worm was found wriggling around in an Australian woman’s brain recently, you could be forgiven for thanking your lucky stars you don’t have a similar parasite living inside you. But it turns out the chances are much more likely than you might think. More than 1 billion people are thought to have threadworms, a type of invertebrate also known as the pinworm, as per a 2019 study by NCBI. Threadworms grow to around 1cm in length and are specific to human hosts. They infect the small intestine, make your bottom feel itchy and can be passed from person to person. They are a common type of infection in the UK, particularly in children under the age of 10. Threadworms are white and look like small pieces of thread – they are usually spotted in people’s poo. According to the NHS website, they can make people irritable and cause them to wake up at night. When things get really bad, they can cause weight loss. The woman in Australia’s worm, by contrast, was found in her brain, and surgeons needed to get it out manually. “Everyone [in] that operating theatre got the shock of their life when [the surgeon] took some forceps to pick up an abnormality and the abnormality turned out to be a wriggling, live 8cm light red worm," said infectious diseases doctor Sanjaya Senanayake, according to the BBC. If you get threadworms, you won’t need to have brain surgery, fortunately. You can buy medicine (mebendazole) for threadworms from pharmacies, according to NHS online. This is usually a chewable tablet or liquid you swallow. The medicine kills the threadworms, but it does not kill the eggs. Eggs can live for up to 2 weeks outside the body. There are other types of worms you can catch, however. Tapeworms, roundworms and hookworms are all relatively common parasites that you can catch from eating raw or undercooked meat. They can also be caught from inadvertently touching infected poo. Roundworms look more like earthworms, tapeworms are long, pale yellow and flat and hookworms, somewhat horrifically, cause a red, worm-shaped rash beneath the skin. Vincent Ho, associate professor and clinical academic gastroenterologist at Western Sydney University in Australia, said that there are four things you can do to avoid these nasty little critters. “Avoid undercooked or raw pork. Freezing meat first may reduce risks (though home freezers may not get cold enough) and it must be cooked to a high internal temperature. Avoid pork if you are travelling in places with poor sanitation,” he said in an article for The Conversation. “Avoid jumping or diving into warm fresh bodies of water, especially if they are known to carry Naegleria fowleri. Although only a handful of cases are reported each year, you should assume it’s present. “Practise good hand hygiene to reduce the risk of rare and common infections. That means washing hands thoroughly and often, using soap, scrubbing for at least 20 seconds, rinsing and drying well. Clip and clean under fingernails regularly. “To avoid soil-borne parasites, wear shoes outside, especially in rural and remote regions, wash shoes and leave them outside.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-29 23:26

Shark that can live for 500 years found by fishermen leaving scientists baffled
Scientists are shocked having found a shark normally found deep in the Arctic, 4,000 miles away in the warm Caribbean. According to findings published in the Marine Biology journal, the Greenland shark turned up off the coast of Belize in Central America while a team of researchers were out on a boat catching and tagging tiger sharks. Devanshi Kasana, a PhD student at Florida International University, was part of the crew working with local fishermen at the time when she realised that a particular fish on the end of their fishing lines looked like a "rather sluggish creature". She added: "At first, I was sure it was something else, like a six-gill shark that are well known from deep waters off coral reefs. I knew it was something unusual and so did the fishers, who hadn’t ever seen anything quite like it in all their combined years of fishing.” Kasana took a photo of the animal and sent it to her advisor, who said it appeared to be a Greenland shark, which was soon confirmed by experts on the specific species. Another expert thought it might be a hybrid between a Greenland and a Pacific sleeper shark. Omar Faux, a fisherman on the boat, said: "I am always excited to set my deep water line because I know there is stuff down there that we haven’t seen yet in Belize, but I never thought I would be catching a Greenland shark." This is the first time that the large shark has been seen in the western Caribbean, off the world's second-largest coral reef, according to the university. The half-blind Greenland shark is rarely seen and is the longest-living vertebrae animal known, with some age estimates between 250 and 500 years old. Weird... Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-29 19:49

Live worm discovered in woman's brain in a worrying world first
A worm has been found living inside a woman’s brain, in a horror-movie-style world first. Doctors in Canberra, Australia, were left stunned after they pulled the 8cm (3in) parasite from the patient’s damaged frontal lobe tissue during surgery last year. "Everyone [in] that operating theatre got the shock of their life when [the surgeon] took some forceps to pick up an abnormality and the abnormality turned out to be a wriggling, live 8cm light red worm," said infectious diseases doctor Sanjaya Senanayake, according to the BBC. "Even if you take away the yuck factor, this is a new infection never documented before in a human being." Senanayake and his colleagues believe the parasite could have been in there for up to two months. The patient, a 64-year-old woman from New South Wales, was first admitted to her local hospital in late January 2021 after suffering three weeks of abdominal pain and diarrhoea, followed by a constant dry cough, fever and night sweats, The Guardian reports. By 2022, her symptoms extended to forgetfulness and depression, and she was referred to Canberra Hospital, where an MRI scan of her brain revealed “abnormalities” that required surgery. “The neurosurgeon certainly didn’t go in there thinking they would find a wriggling worm,” Senanayake told the paper. “Neurosurgeons regularly deal with infections in the brain, but this was a once-in-a-career finding. No one was expecting to find that.” The team at the hospital sent the worm to an experienced parasite researcher who identified it as an Ophidascaris robertsi. This type of roundworm is commonly found in carpet pythons – non-venomous snakes that are ubiquitous across much of Australia. Writing in the journal Emerging Infectious Diseases, Mehrab Hossain, a parasitologist, said she suspected that the patient became an "accidental host" to the worm after cooking with foraged plants. The 64-year-old was known to have often collected native grasses from around her lakeside home, Senanayake told The Guardian. He and his co-workers have concluded that the woman was probably infected after a python shed eggs from the parasite via its faeces into the grass. By touching the plants, she may then have transferred the eggs into her own food or kitchen utensils. Fortunately, the unlucky and unique patient is said to be making a good recovery. However, Senanayake told the BBC that her case should serve as an important warning to society more broadly. "It just shows as a human population burgeons, we move closer and encroach on animal habitats. This is an issue we see again and again, whether it's Nipah virus that's gone from wild bats to domestic pigs and then into people, whether its a coronavirus like Sars or Mers that has jumped from bats into possibly a secondary animal and then into humans,” he said. "Even though Covid is now slowly petering away, it is really important for epidemiologists… and governments to make sure they've got good infectious diseases surveillance around." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-29 15:49
