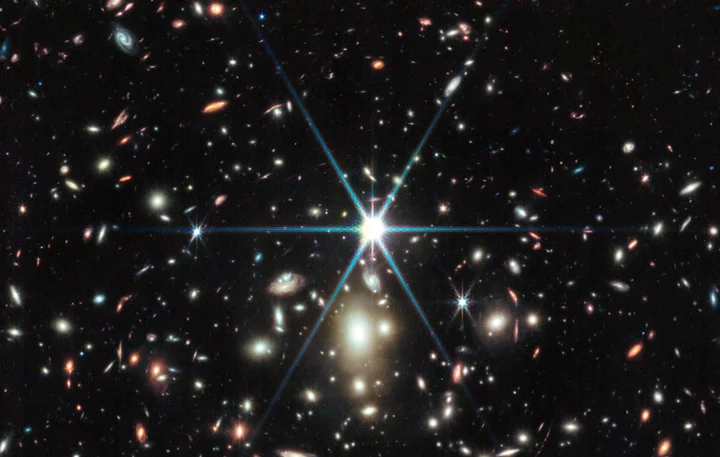
The Hubble Space Telescope shocked astronomers when it discovered Earendel, a star so old, it existed perhaps just 1 billion years after the big bang.
Now the experts have used the James Webb Space Telescope, Hubble's powerful infrared partner, to take a gander, and its first look has revealed even more details about the star. To scientists' surprise, Earendel might actually have a cooler, redder space companion: another star. Because the expansion of the universe has stretched the other lightsource to wavelengths longer than Hubble can sense, only Webb could find those clues.
"Astronomers did not expect Webb to reveal any companions of Earendel since they would be so close together and indistinguishable in the sky," according to the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore.
SEE ALSO: Webb telescope just found something unprecedented in the Orion NebulaStudying a star like Earendel is valuable because it holds secrets to how the universe, thought to be 13.8 billion years old, began and evolved. With Webb, the leading space observatory run by NASA and the European and Canadian space agencies, scientists have gained new insights into the star’s type and the galaxy around it known as the Sunrise Arc. Future research by the telescope could reveal even more information about the star's brightness, temperature, and composition.
The new findings indicate Earendel, meaning "morning star" in Old English, is a massive B-type star, more than double the temperature of the sun and about 1 million times brighter.
Hubble was able to detect Earendel last year due to a quirk of nature known as gravitational lensing. This phenomenon happens when a celestial object has such a massive gravitational pull, it warps the time and space around it.
Want more science and tech news delivered straight to your inbox? Sign up for Mashable's Light Speed newsletter today.
NASA often uses the analogy of a bowling ball placed on a foam mattress or trampoline to illustrate how the fabric of spacetime bends. Light that would otherwise travel straight curves and gets distorted as it passes through the warped spacetime.
Gravitational lensing even has the potential to replicate objects, the way a funhouse mirror can create multiple irregular copies of images.
Hubble and Webb were able to detect Earendel in Sunrise Arc last year due to a quirk of nature known as gravitational lensing. Credit: NASA / ESA / CSAIn this case, Earendel only appears once, but the galaxy cluster WHL0137-08, about 28 billion light-years from Earth, is acting like a colossal magnifying glass. It warps spacetime, allowing scientists to see even more distant objects in the cosmos. The extra prescription strength of a gravitational lens can help extend the view of telescopes to see even earlier galaxies.
Astronomers are now adept at spotting the telltale tricks of gravitational lensing, but that wasn't always true. In 1987, an enormous blue arc thought to be hundreds of trillions of miles long was first considered one of the largest objects ever detected in space. Later that year, scientists sorted out, with the help of Einstein's General Theory of Relativity, that they were in fact looking at an optical illusion, distorted by a galaxy cluster. The New York Times' published a story about the "bizarre" implication of their findings, titled "Vast Cosmic Object Downgraded to a Mirage."
Since Hubble’s discovery of Earendel, Webb has detected other extremely distant (and, thus, old) stars using the gravitational lensing technique, though none quite so far away. Another group of scientists discovered one nicknamed Quyllur, a red giant star observed about 3 billion years after the big bang.
"The research team has cautious hope that this could be a step toward the eventual detection of one of the very first generation of stars," the institute says, "composed only of the raw ingredients of the universe created in the big bang — hydrogen and helium."