
Study discovers vast numbers of women experience mental health issues because of period pain
A study has shown that millions of women and girls experience debilitating periods, that even cause mental health problems. A survey of 3,000 women and girls in the UK aged 16 to 40 for the Wellbeing of Women charity found that 86 per cent had had mental health problems, such as depression, anxiety and mood changes, in relation to their period, Meanwhile, of those surveyed, 96 per cent had experienced period pain, with 59 per cent saying their pain was severe. 91 per cent had experienced heavy periods, with 49 per cent saying their bleeding was severe. Even though these are common symptoms in women and girls with gynaecological conditions such as endometriosis, adenomyosis, fibroids and polycystic ovary syndrome, the report found that 51 per cent of respondents felt their healthcare professional had failed to take their problems seriously, and 82 per cent said they needed better access to accurate information on period problems. A further one-third never seek medical help, and more than half say their symptoms are not taken seriously, despite other symptoms including pain, heavy bleeding and irregular cycles. Prof Dame Lesley Regan, the chair of Wellbeing of Women, said: “It’s simply unacceptable that anyone is expected to suffer with period symptoms that disrupt their lives, including taking time off school, work, or their caring responsibilities, all of which may result in avoidable mental health problems. “Periods should not affect women’s lives in this way. If they do, it can be a sign of a gynaecological condition that requires attention and ongoing support – not dismissal.” Wellbeing of Women has launched its “Just a Period” campaign, which Regan said aims to address “the many years of medical bias, neglect and stigma in women’s health”. This includes tips on how to get the most out of seeing your GP and what women should do if they feel they have been dismissed by health professionals. Responding to the findings, Dr Ranee Thakar, the president of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, said: “All too often women are living with debilitating symptoms, waiting to receive support or treatment for far longer than they should. “Access to high-quality information and support about periods, gynaecological conditions and their symptoms is vital to ensuring that women and girls get the help that they need at the right time.” Caroline Nokes, the Conservative MP and chair of the women and equalities committee, which is conducting an inquiry into reproductive and gynaecological health, said: “There is a terrible phrase: ‘Well, it’s just a period, why are you making a fuss about that? Can’t you just get on with it?’ Yet many women and girls are experiencing horrendous period symptoms and gynaecological conditions. Endometriosis alone affects 1.5 million women in the UK and costs the economy £8.2bn. Now is the time for change.” Anneliese Dodds, the shadow secretary of state for women and equalities, said: “Over the past few years, we have opened up the conversation around the menopause, and now we need to see this change with periods as well.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-14 17:56
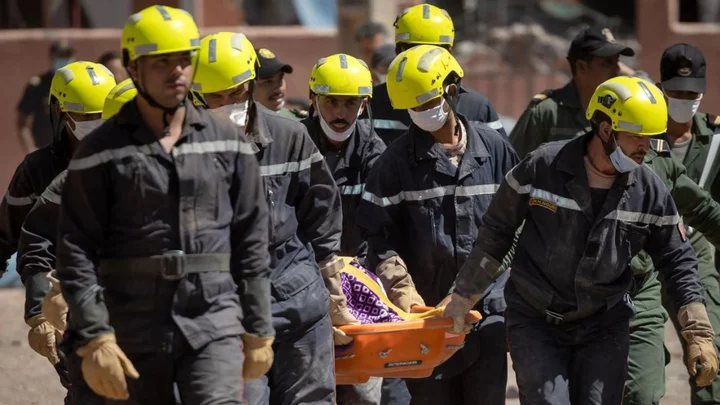

'Earthquake lights' video seen moments before Morocco tragedy fuel age-old theory
With the tragedy and horror wreaked in Morocco last week, it's unsurprising that people’s focus hasn’t been on the skies. And yet, Friday’s devastating earthquake, has also sparked renewed interest in a mysterious aerial phenomenon. Footage shared to social media just moments before the 6.8-magnitude tremor struck the High Atlas mountains appears to show blinding lights flashing across the sky. Experts have suggested that the jaw-dropping sight is evidence of an enigmatic natural occurrence called “earthquake lights”. Reports of these bright flashes go back centuries. And yet, very little is known about them, to the point that scientists aren’t even sure they’re real. Indeed, some experts have concluded that there isn’t sufficient proof to support their existence, the United States Geological Survey notes. Nevertheless, “people have wondered about them forever," Karen Daniels, a physicist at North Carolina State University, told the New York Times. "It's one of those persistent mysteries that hang around and never quite get nailed." The issue with studying earthquake lights is that since earthquakes are impossible to predict, so are any preceding celestial pyrotechnics. Not knowing when or where they will occur means researchers can’t preemptively install the necessary equipment needed to detect them. Essentially, the only evidence we have comes from eyewitness accounts and, more recently, video recordings. And there is an abundance of the former, with a 2014 study noting that aerial luminous phenomena were reported in relation to 65 earthquakes which occurred in Europe and America over a period of 200 years. These descriptions of earthquake lights vary in their details, with some recalling on-and-of lightning-style flashes, and others minutes-long glows of different colours. “All of these have been reported by observers,” John Ebel, a seismologist at Boston Collegel told the NYT. “Which ones are actually true, and which ones are products of their imagination, we can’t really say.” One theory behind the formation of earthquake lights is that they are the result of friction between tectonic plates generating electricity. However, most experts are unconvinced by this hypothesis, including Dr Daniels. She told the NYT: “Rock on rock is not a situation where people have been able to generate large charge separation. And so it just doesn’t seem like a very good explanation for what people see.” Other scientists have suggested electrical arcing from power lines shaken by earthquakes could be responsible for the sky flares. But Dr Daniels acknowledged it’s still possible that there’s no link at all between the lights and tectonic events. “We’re comforted by things that we can understand, and we’re scared by things we don’t,” she pointed out. “I think that’s part of the reason we’re so fascinated by this phenomenon.” Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-13 21:59
Science news - live: Hidden oceans and moon structures discovered
It feels like this year, more than any other, we’re seeing a stream of science stories that continue to blow our minds. Every day is a school day online in 2023, and a host of studies, research papers and headline-making breakthroughs have completely changed our understanding of the world around us at every turn. There have been missions to the moon and findings about our planet which could turn everything we thought we knew on its head – not to mention baffling hearings on UFOs taking place in the US congress. These are the biggest science stories so far this year that have caught our attention in a big way. 'Alien corpses' unveiled in Mexico divide conspiracy theorists Christmas has come early for UFO watchers, with the alleged corpses of real-life aliens displayed for the world to see. The startling revelation came during a congress hearing in Mexico City on Tuesday, titled the Public Assembly for the Regulation of Unidentified Anomalous Aerial Phenomena (UAP). During the session, which was streamed online, Mexican ufologist Jaime Maussan presented what he claimed were two perfectly preserved “non-human entities”. Read more here. Buy now , Massive ocean discovered beneath the Earth's crust containing more water than on the surface People are only just realising that there’s a massive ocean hidden under the Earth’s crust. It turns out there’s a huge supply of water 400 miles underground stored in rock known as 'ringwoodite'. Scientists previously discovered that water is stored inside mantle rock in a sponge-like state, which isn’t a liquid, solid or a gas, but instead a fourth state. Read more here. Buy now , Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-09-13 19:25

Scientists discover new Black holes that could be creeping up on Earth
A new study has revealed that black holes could be lurking much closer to Earth than anticipated. A black hole in space is when "gravity pulls so much that even light can not get out," NASA explains. "The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying." Due to no light being present, they are invisible. Only special tools can pick up on them. There are said to be around 10 million to 1 billion mass black holes in the Milky Way, according to Science Alert. However, astrologers only know of about 20 of them. Now, a recent study has revealed that they could be a lot closer to Earth than previously thought after investigating the Hyades cluster, "a group of stars located 150 light-years away". In a statement, astrophysicist Stefano Torniamenti of the University of Padua explained: "Our simulations can only simultaneously match the mass and size of the Hyades if some black holes are present at the centre of the cluster today (or until recently). The Hyades with hundreds of stars is said to be approximately 625 million years old. Due to its packed environment, "higher rates of collisions and mergers" are expected. At 153 light-years away, it is considered the closest star cluster to Earth. Researchers were able to observe two or three black holes in the Hyades, which are either still present or ejected less than 150 million years ago and hovering around the outskirts. "This observation helps us understand how the presence of black holes affects the evolution of star clusters and how star clusters in turn contribute to gravitational wave sources," Professor Mark Gieles of the University of Barcelona said. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-12 22:56
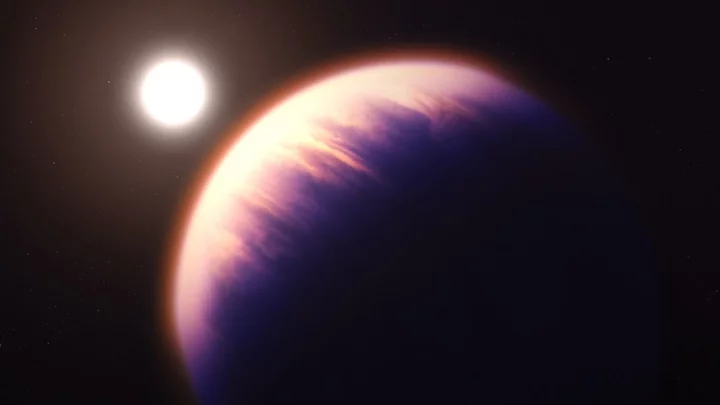

Scientists discover huge exoplanet 120 light years from Earth that ‘could contain signs of life’
An exoplanet more than eight times the size of Earth and potentially habitable has been discovered by scientists. Exoplanet K2-18 b was detected by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and piqued scientists’ interest after data suggested it may be covered in an ocean and have a hydrogen-rich atmosphere that could support life. Scientists are also encouraged by a hint of the detection of the molecule dimethyl sulphide (DMS). On Earth, DMS is only produced by microbial life, but the team has yet to confirm the detection and search for evidence of biological activity. The groundbreaking discovery of K2-18 b may see the exoplanet come under the unique classification of a “Hycean” planet – ones which are candidates for life thanks to their hydrogen-rich atmospheres and water cover. The amount of methane and carbon dioxide combined with the shortage of ammonia suggests there may be a water ocean underneath a hydrogen-rich atmosphere in K2-18 b. K2-18 b lies within the constellation of Leo and orbits a dwarf star called K2-18. It lies around 120 light years away from Earth and is within the habitable zone. However, scientists added that this does not necessarily mean it can support life. Nikku Madhusudhan, an astronomer at the University of Cambridge and lead author of the paper, explained: “Our findings underscore the importance of considering diverse habitable environments in the search for life elsewhere. “Traditionally, the search for life on exoplanets has focused primarily on smaller rocky planets, but the larger Hycean worlds are significantly more conducive to atmospheric observations.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-12 17:22

Black holes may lie even closer to us than we thought, new study finds
A new study has revealed that black holes could be lurking much closer to Earth than anticipated. A black hole in space is when "gravity pulls so much that even light can not get out," NASA explains. "The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying." Due to no light being present, they are invisible. Only special tools can pick up on them. There are said to be around 10 million to 1 billion mass black holes in the Milky Way, according to Science Alert. However, astrologers only know of about 20 of them. Now, a recent study has revealed that they could be a lot closer to Earth than previously thought after investigating the Hyades cluster, "a group of stars located 150 light-years away". In a statement, astrophysicist Stefano Torniamenti of the University of Padua explained: "Our simulations can only simultaneously match the mass and size of the Hyades if some black holes are present at the centre of the cluster today (or until recently). The Hyades with hundreds of stars is said to be approximately 625 million years old. Due to its packed environment, "higher rates of collisions and mergers" are expected. At 153 light-years away, it is considered the closest star cluster to Earth. Researchers were able to observe two or three black holes in the Hyades, which are either still present or ejected less than 150 million years ago and hovering around the outskirts. "This observation helps us understand how the presence of black holes affects the evolution of star clusters and how star clusters in turn contribute to gravitational wave sources," Professor Mark Gieles of the University of Barcelona said. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-11 20:16
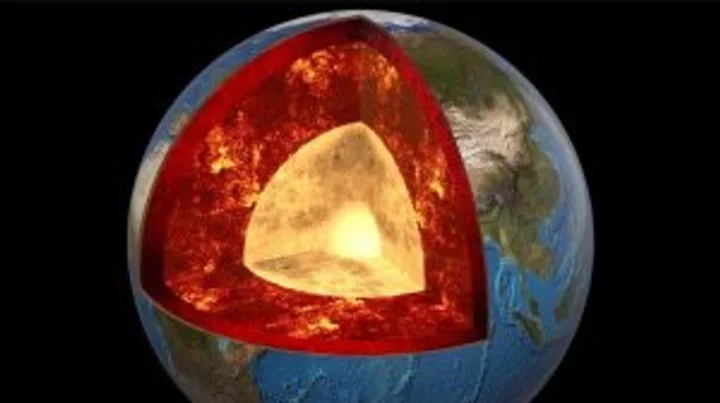
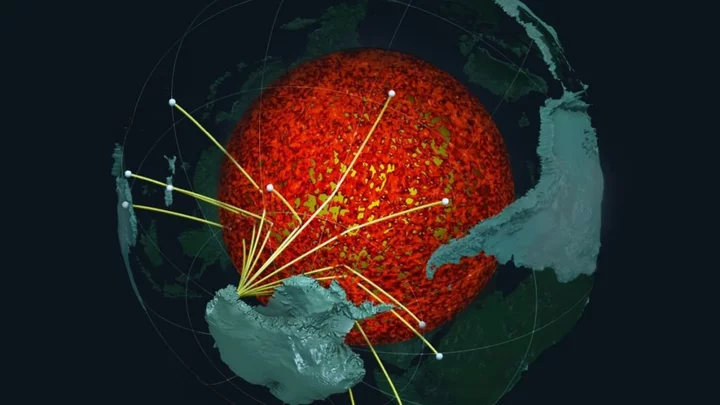
'Mountains' taller than Everest discovered on 'ancient structure' around Earth's core
A new study into the Earth beneath our feet has discovered that an ancient ocean floor structure could be wrapped around the planet's core which could be taller that Mount Everest in some areas. A brand new high-resolution mapping of the core has uncovered things that scientists previously didn't know according to a study that was first published in April. The discovery found that a thin but dense layer sits at around 2,900 kilometers below the surface at the Core Mantle Boundary where rocks meet the molten outer core of the planet. Geologist Samantha Hansen from the University of Alabama is quoted in the study saying: "Seismic investigations, such as ours, provide the highest resolution imaging of the interior structure of our planet, and we are finding that this structure is vastly more complicated than once thought." She adds: "Our research provides important connections between shallow and deep Earth structure and the overall processes driving our planet.” Hansen and her team conducted the research from 15 different stations in Antarctica by using seismic waves created by Earthquakes to create a map of what the inside of the planet looks like. The team identified the unexpected energy within seconds of the boundary-reflected wave from the seismic data. The findings show that although the layer is very thin it does spread for many, many kilometers and has been called the ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZs) due to its strong wave speed reductions. Due to the properties of the ULVZs the experts believe that the layer could vary dramatically in height. Geophysicist Edward Garnero from Arizona State University adds: "The material's thickness varies from a few kilometers to [tens] of kilometers. This suggests we are seeing mountains on the core, in some places up to five times taller than Mt. Everest." These underground mountains could play a significant role in how heat escapes from the Earth's core and power magnetic fields and volcanic eruptions. The team's studies suggest that the layer could encase all of the core but further research will have to be carried out to determine if that is the case. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-10 19:26
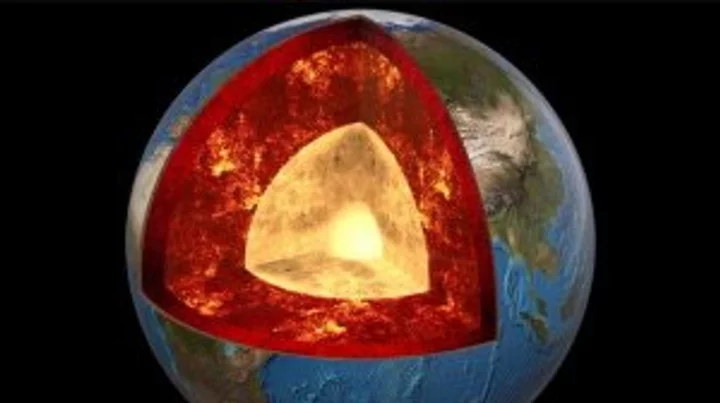
Underground 'mountains' discovered on Earth's core five-times taller than Mt. Everest
A new study into the Earth beneath our feet has discovered that an ancient ocean floor structure could be wrapped around the planet's core which could be taller that Mount Everest in some areas. A brand new high-resolution mapping of the core has uncovered things that scientists previously didn't know according to a study that was first published in April. The discovery found that a thin but dense layer sits at around 2,900 kilometers below the surface at the Core Mantle Boundary where rocks meet the molten outer core of the planet. Geologist Samantha Hansen from the University of Alabama is quoted in the study saying: "Seismic investigations, such as ours, provide the highest resolution imaging of the interior structure of our planet, and we are finding that this structure is vastly more complicated than once thought." She adds: "Our research provides important connections between shallow and deep Earth structure and the overall processes driving our planet.” Hansen and her team conducted the research from 15 different stations in Antarctica by using seismic waves created by Earthquakes to create a map of what the inside of the planet looks like. The team identified the unexpected energy within seconds of the boundary-reflected wave from the seismic data. The findings show that although the layer is very thin it does spread for many, many kilometers and has been called the ultra-low velocity zone (ULVZs) due to its strong wave speed reductions. Due to the properties of the ULVZs the experts believe that the layer could vary dramatically in height. Geophysicist Edward Garnero from Arizona State University adds: "The material's thickness varies from a few kilometers to [tens] of kilometers. This suggests we are seeing mountains on the core, in some places up to five times taller than Mt. Everest." These underground mountains could play a significant role in how heat escapes from the Earth's core and power magnetic fields and volcanic eruptions. The team's studies suggest that the layer could encase all of the core but further research will have to be carried out to determine if that is the case. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-09 19:54
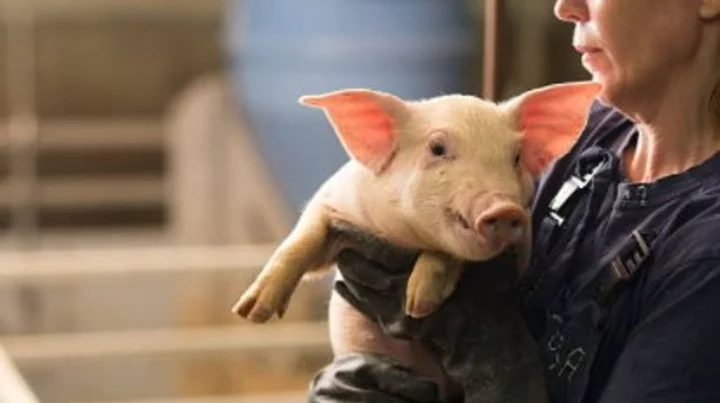

Scientists grow human kidneys inside a pig for the first time
Scientists have grown human kidneys in pigs, for the very first time. Researchers at the Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Wuyi University created human-pig chimeric embryos containing a combination of human and pig cells. When they transferred into 13 surrogate pig mothers, they developed kidneys that contained mostly human cells at a rate of 50 to 60 per cent, giving hope for potential transplants in the future. “Rat organs have been produced in mice, and mouse organs have been produced in rats, but previous attempts to grow human organs in pigs have not succeeded,” said the senior author Liangxue Lai. “Our approach improves the integration of human cells into recipient tissues and allows us to grow human organs in pigs.” The kidneys were not entirely human as they included vasculature and nerves made mostly from pig cells, meaning they could not be used for transplantation in their current form, but it is still a pretty impressive step. And apart from the kidneys, the embryos were dominated by pig cells, with very few human cells in the brain or central nervous system. Making brains using human and pig cells is very controversial for ethical reasons, so there are tight regulations for this kind of research. Meanwhile, pig cells tend to outcompete human cells during development, so previous experiments have created embryos that are almost entirely pig. The latest work, published in Cell Stem Cell, overcame this by genetically engineering a single-cell pig embryo so that it lacked two genes needed for kidney development. This created a gap within the embryo that could be filled by human cells. “We found that if you create a niche in the pig embryo, then the human cells naturally go into these spaces,” said Prof Zhen Dai of Guangzhou Institutes of Biomedicine and Health, another senior author. The scientists said that being able to incubate a fully human kidney inside a pig would be likely to take many years. “We would probably need to engineer the pigs in a much more complex way and that also brings some additional challenges,” said Miguel Esteban, also of the Guangzhou institute and a senior author. A central challenge would be to allow human nerves and vasculature to develop within the target organ without nerve cells developing in the central nervous system that could lead to a humanised brain. “Even theoretically it’s not clear how you’d do that,” said Ilic. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-08 19:49
Human embryo created without using sperm or eggs
Scientists in Israel have created a model of a human embryo from stem cells, without using sperm, eggs or a womb. A team at Israel's Weizmann Institute of Science made the model, which resembles an embryo at day 14, when it acquires internal structures but before it lays down the foundations for body organs, and the work was published in the journal Nature. But the scientists involved said it would take a long time yet to create an embryo from scratch. Team leader Jacob Hanna said the team took stem cells derived from adult human skin cells, as well as others cultured in the lab, then reverted the cells to an early state.They then manipulated them to make a model of an embryo, rather than an actual or synthetic one. "The question is, when does an embryo model become considered an embryo? When that happens, we know the regulations. At the moment we are really, really far off from that point," Hanna said. However, they said the work could open the door to new ways to test the effect of drugs on pregnancies, better understand miscarriages and genetic diseases, and maybe grow transplant tissues and organs. "They are not identical. There are differences from human embryos, but still, this is the first time, if you open an atlas or a textbook, you can say - yeah I can really see the similarity between them," said Hanna. "In about 1 percent of the aggregates we can see that the cells start differentiating correctly, migrating and sorting themselves into the correct structure, and the farthest we could get is day 14 in human embryo development," he said. Their next goal, Hanna said, is to advance to day 21 and also reach a threshold of a 50 per cent success rate. Magdalena Żernicka-Goetz, a professor of development and stem cells at the University of Cambridge, said the study joins six other similar human embryo-like models published from teams around the world this year, including from her lab. "None of these models fully recapitulate natural human development but each adds to ways in which many aspects of human development can now be studied experimentally," she said. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-08 18:26
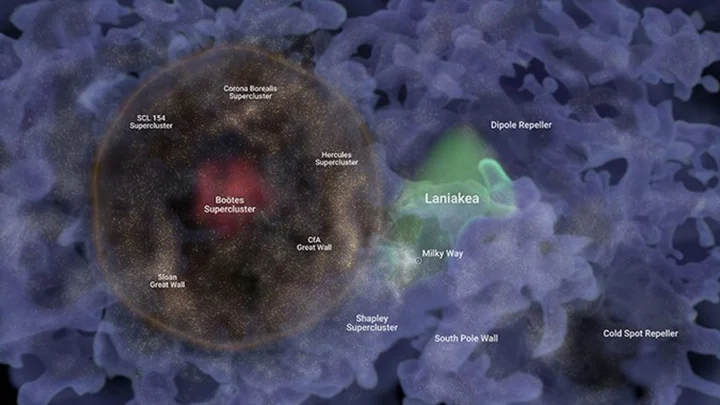
Massive bubble of galaxies could be ‘fossil of the Big Bang’, say scientists
A huge bubble of galaxies that is one billion lightyears across could be a remnant of the ripples caused by the Big Bang, according to astronomers who have mapped the structure. The structure, named Hoʻoleilana by University of Hawaii scientists, is thought to have been caused by so-called Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAOs). These were ripples in the particles of the early Universe in the period following the Big Bang, when planets, solar systems and galaxies were not yet fully formed. As the ripples went outward, they created areas of density in the particles, causing bubble-like structures in which galaxies eventually coalesced. Until now, the BAOs were just a prediction – part of the wider Big Bang theory. No specific structures in the Universe had been found which mimicked their patterns. But Hoʻoleilana fits the description of these huge cosmic bubbles perfectly, according to Brent Tully, who led the study at the University of Hawaii’s Institute for Astronomy. “We were not looking for it. It is so huge that it spills to the edges of the sector of the sky that we were analyzing,” he said. “As an enhancement in the density of galaxies it is a much stronger feature than expected. The very large diameter of 1bn light years is beyond theoretical expectations. “If its formation and evolution are in accordance with theory, this BAO is closer than anticipated, implying a high value for the expansion rate of the universe.” The bubble is absolutely huge. It is made up of several superclusters, structures which themselves are thought to be among the Universe’s largest arrangements of matter. This includes the Hercules Supercluster, the Corona Borealis Supercluster and the Sloan Great Wall. All of these structures contain thousands of galaxies. In the middle of Hoʻoleilana sits the Bootes Supercluster and the Bootes Void, an immense space of nothingness which is an incredible 330m lightyears across. Daniel Pomarede, from the CEA Paris-Saclay University, who contributed to the research, said: “It was an amazing process to construct this map and see how the giant shell structure of Ho’oleilana is composed of elements that were identified in the past as being themselves some of the largest structures of the universe.” The research was published on 5 September in The Astrophysical Journal. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-07 20:00

India’s Moon lander just detected movement below the lunar surface
India’s Vikram lunar lander has recorded movement below the surface of the Moon – but it’s probably not aliens. Experts think the movement is seismic activity – the lunar equivalent of earthquakes. It is the first time humans have detected the so-called moonquakes since the 1970s. The new activity was recorded by the Vikram lander’s onboard instrument for lunar seismic activity, a piece of kit designed “to measure ground vibrations generated by natural quakes, impacts, and artificial events,” the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) said. India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission saw it land the Vikram and its sister craft, the Pragyan rover, last month, becoming the first nation to land near the Moon’s little-explored South Pole. It also makes India just the fourth nation to land on the Moon, alongside the US, the former USSR and China. The seismic activity is the first recorded since the US Apollo programme, which ended in 1977. Those recordings yielded valuable data about the Moon’s makeup. Scientists have been able to theorise that the Moon has an inner core which is much less dense than the Earth’s and which is about 500km across. On Earth, seismic activity is caused by the shifting of the planet’s tectonic plates. But on the Moon, things are a bit different. The quake could be caused by thermal activity from the Sun, or by tidal stresses caused by Earth’s gravity, cracking the planet and causing the pieces to rub together. The team noted that the event is currently under investigation. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-07 19:20
