Scientists discover strange 'mathematical pattern' in the human body
The human body is a marvel of science and researchers have discovered a strange reoccurring mathematical pattern within its cells. Our bodies are made up of a massive variety of individual cells with countless different functions, from neurons in our nervous system to the oxygen carriers that all work in harmony to keep us alive. Experts from scientific research institutions in Germany, Canada, Spain, and the US have worked together on a study to determine just how many cells of each type there are in the human body and the results are staggering. They found that most adult males possess around 36 trillion cells, while adult females have in the region of 28 trillion cells. For a 10-year-old child, they have around 17 trillion. Interestingly though, scientists discovered that, regardless of the total number of cells, if they are grouped according to their function, the proportions for each individual remain the same. The researchers explained in their findings: “These patterns are suggestive of a whole-organism trade-off between cell size and count and imply the existence of cell-size homeostasis across cell types.” Scientists believe there is a natural balancing act at play between different cell types with new cells being produced to maintain the balance. The body produces fewer larger cells (such as muscle fibres) and more smaller cells (like blood cells). It is hoped that future studies will be able to uncover exactly how this happens and how bodies seem to naturally regulate cells. They explained that all cells are perfectly sized for their roles and any deviation from their scale can indicate the presence of disease. Experts have made their data, analysis and results public in the hopes that future studies into biology will be able to utilise their research. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-22 23:15
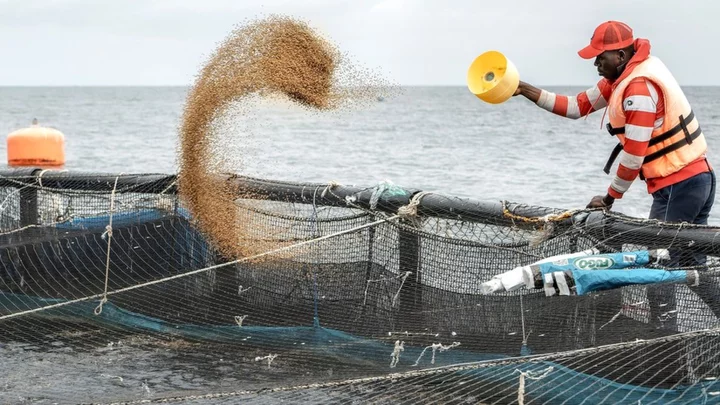

Despite risks fish farms are booming in Africa
Farming fish has seen rapid growth in Africa but it can be an expensive, high-risk operation.
2023-09-22 07:50
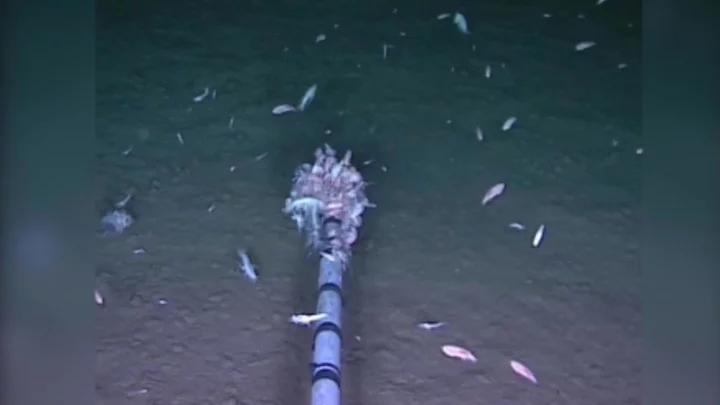

Scientists have found a novel virus at the bottom of the ocean
Scientists have discovered a new virus in the Pacific that is thought to be the deepest ever found in Earth’s oceans. The so-called bacteriophage virus infects and replicates inside bacteria, and was found in the Mariana Trench, which is the Pacific’s deepest point. Bacteriophages are among the world’s most abundant life forms, and are important for regulating population sizes in the oceans and releasing nutrients. This one, the catchily named vB_HmeY_H4907, was picked up at 8,900 metres below sea level. That is still some way off the 11,000 metre floor of the trench. Min Wang, a marine virologist from the Ocean University of China, said: “To our best knowledge, this is the deepest known isolated phage in the global ocean.” “Wherever there’s life, you can bet there are regulators at work. Viruses, in this case.” Scientists think this virus is likely to be distributed widely in the world’s oceans, despite the fact it has only been discovered. It has a similar structure to its host bacteria group halomonas. These are usually found in sediments and geyser-like openings on the seafloor. They also think the virus is lysogenic, which means it infects the host but does not kill it. Dr Wang said the discovery could inform further research about how viruses survive in the world’s harshest environments. “Extreme environments offer optimal prospects for unearthing novel viruses,” he added. The virus was found in the so-called hadal zone, which the study’s authors said is “the planet’s least explored and most mysterious environment, and it is the deepest habitat for life on Earth’s surface”. The area is named after Hades, the Greek god of the underworld. Researchers wrote in the study: “These findings expand our understanding of the phylogenetic diversity and genomic features of hadal lysogenic phages, provide essential information for further studies of phage-host interactions and evolution, and may reveal new insights into the lysogenic lifestyles of viruses inhabiting the hadal ocean.” The findings were published in the journal Microbiology Spectrum. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 20:58

Scientists issue warning about asteroid heading to Earth with force of 24 atomic bombs
Scientists are on alert after NASA confirmed there is a chance an asteroid the size of the Empire State Building could come smashing into Earth. The asteroid is named Bennu after the ancient Egyptian bird god and has been on the space agency’s radar for a long time as they try to prevent it from coming crashing into our planet. Bennu has been categorised as one of the two “most hazardous known asteroids” and, despite the chance of impact standing at 1-in-2,700, it could strike the Earth with the force of 24 times that of the largest nuclear bomb – 1,200 megatons of energy. The carbon-based asteroid is approximately 510 metres wide and experts predict that it will come closest to hitting Earth on September 24, 2182. While the asteroid is quite sizeable, it is not quite as sizeable as the six-mile-wide asteroid which almost completely wiped out the dinosaurs. But, NASA warns that Bennu “could cause continental devastation if it became an Earth impactor”. A space mission launched using NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft has successfully taken a sample from Bennu in order for scientists to better understand the potentially dangerous asteroid. On Sunday (24 September) a capsule of the material will be dropped by OSIRIS-REx and returned to Earth where it will be retrieved and the matter inside studied. Davide Farnocchia of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory told the Science Journal: “We improved our knowledge of Bennu's trajectory by a factor of 20.” As scientists work to investigate how much of a risk it could cause, Farnocchia added: “In 2135, we'll know for sure.” Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 20:26

A scientist has discovered when Earth's first continent was formed
A researcher has figured out that the Earth’s first continent was formed 3bn years ago, in a new paper that sheds fresh light on the early stages of the planet’s life. Jane Greaves, an astronomy professor in the School of Physics and Astronomy at Cardiff University in Wales, was examining continent formation on distant stars and planets. It is thought that exoplanets with continents that formed in a similar way to Earth’s are more likely to be habitable, and perhaps even contain alien life. In the process, she calculated when several distant planets’ continents were born, as well as those a little closer to home. Continents on Earth sit on top of the planet’s hot, viscous mantle. Heat from the inner core stops the mantle from solidifying. The reason the core is hot is because it contains radioactive elements that came from neutron star collisions billions of years ago such as forms of Uranium, Thorium and Potassium. By analysing how many materials like this are present on Earth and on other planets, we are also able to estimate when the continents formed. On Earth, that was about 9.5 billion years since the beginning of the universe. Meanwhile, in Greaves' sample, the first continents appeared 2bn years before Earth’s on the exoplanets of younger, so-called thin disk stars. Older, thick disk stars analysed in her work produced rocky planets with continents that appeared even earlier: about 4 to 5bn years before Earth’s. “The outlook seems very promising for finding rocky exoplanets with continents, given that nearby Sun-like stars have already produced a few candidate hosts,” she wrote. The study, “When were the First Exocontinents?” is published in Research Notes of the American Astronomical SocietySign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-21 17:15
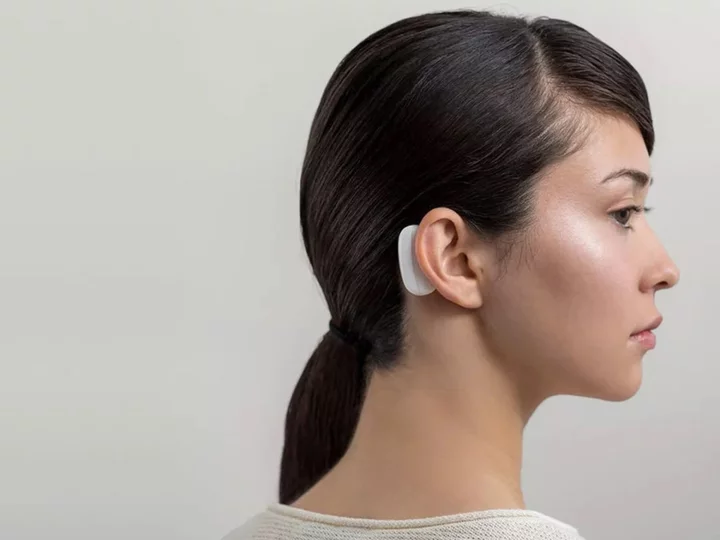

Elon Musk to start human trials with brain chip startup Neuralink
Elon Musk’s brain chip startup Neuralink has begun recruiting for its first human trials, having previously tested the technology on pigs and monkeys. Neuralink’s brain-computer interface received approval in May from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to test its technology on humans, which the company hopes can help people with brain disorders and spinal injuries. “We’re excited to announce that recruitment is open for our first-in-human clinical trial,” Neuralink posted on X, formerly known as Twitter. “If you have quadriplegia due to cervical spinal cord injury or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), you may qualify.” The study will assess the safety of both the wireless chip and the surgical robot used to implant it in the brain. If successful, subjects will be able to control a computer cursor or keyboard using only their thoughts. The ultimate goal for Neuralink, according to Mr Musk, is to not just treat medical patients but augment the ability of humans in order to allow them to compete with advanced artificial intelligence. Implanted chips could provide “enhanced abilities” like greater reasoning and improved vision, while enabling people to perform previously impossible tasks like streaming music directly to their brain. Neuralink has faced criticism from animal rights groups for the treatment of its research subjects at the University of California’s Davis Primate Centre. The Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (PCRM) accused Mr Musk’s startup of subjecting monkeys to “extreme suffering” and providing “inadequate animal care”. Both Neuralink and Mr Musk have denied the allegations, with the tech billionaire claiming last week that research experiments were only carried out on primates that were already close to death. “No monkey has died as a result of a Neuralink implant,” he wrote on X. “First our early implants, to minimise risk to healthy monkeys, we chose terminal monkeys (close to death already).” Read More Elon Musk is ‘unofficial president’ of the US, Netanyahu says Elon Musk says monkeys implanted with Neuralink brain chips were ‘close to death’ First photo emerges of Elon Musk and his baby twins with Neuralink director Elon Musk reveals trillion dollar algorithm that explains everything he does
2023-09-20 20:23

11 Social Media Platforms You Probably Forgot Existed (And Why They Failed)
Still miss your old Friendster account? Discover why that and other once-popular social media platforms got discontinued here.
2023-09-20 20:19
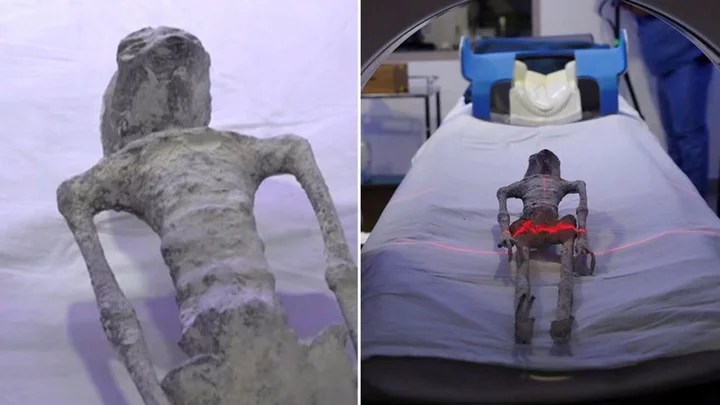

Scientists confirm that one of Mexican aliens is 'alive' after controversial research
Scientists in Mexico have given their verdict on the supposed 'aliens' that were presented to the country's congress last week. Much controversy existed around the aliens who were presented by a man named Jaime Maussan who has previously been accused of using the mummified beings, apparently found in Peru, as part of an elaborate hoax. Despite spawning dozens of memes, the aliens are apparently being treated seriously enough that they have now been studied by scientists who have said that the figures are ‘single skeletons’ and also have 'eggs' inside of them. The two aliens have been named Clara and Mauricio and have reportedly been studied in a lab at the Noor Clinic in Mexico. Lead researcher Dr Jose de Jesus Zalce Benitez, a former navy forensics doctor, who added that as well as being "a single skeleton" the aliens are also a "complete organic being." He also denied that the aliens were part of a hoax and even said that Clara was "alive, was intact, was biological and was in gestation." However, much like the alien bodies themselves, the research has been clouded in controversy and scepticism as the research has yet to be officially verified, with Nasa scientist Dr David Spergel questioning why the findings haven't been made public, as per the BBC. Spergel said: "He said: "If you have something strange, make samples available to the world scientific community and we'll see what's there." Benitez did add in his address at the press conference: "We are facing the paradigm of describing a new species or given the opportunity to accept that there has been contact with other beings, non-humans, that were drawn and marked in the past by diverse cultures throughout the world." Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-09-20 16:18

Musk's Neuralink to start human trial for brain implant chip
Billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk's brain-chip startup Neuralink said on Tuesday that it has received approval from an independent
2023-09-20 02:54

Zuckerberg's philanthropy project plans AI system for life sciences research
Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg's philanthropy venture plans to build a computing system powered by artificial intelligence for life
2023-09-20 00:57

BBC reviews Russell Brand’s time at corporation as YouTube demonetises content
The BBC has announced a review into Russell Brand’s time at the corporation amid the rape and sexual assault allegations made against the comedian. The broadcaster also said on Tuesday that it was removing some content featuring the 48-year-old from its iPlayer and Sounds apps which “now falls below public expectations”. An episode of comedy panel show QI and a Joe Wicks podcast, both featuring Brand as a guest, have been removed, the PA news agency understands. YouTube had earlier announced that the Google-owned company has stopped Brand making money on its platform because he was “violating” its “creator responsibility policy”. Brand has strongly denied the allegations, which also include claims of controlling, abusive and predatory behaviour. A spokesperson for podcasting platform Acast confirmed to PA on Tuesday that advertisements were turned off “immediately” for Brand’s Under The Skin podcast following the allegations. In a long-arranged Q and A with BBC staff on Tuesday, the corporation’s director general Tim Davie was quizzed about how it was responding following accusations about Brand’s time on BBC Radio 2 and BBC Radio 6 Music between 2006 and 2008. The Times reported on Monday that a woman claims Brand used the BBC’s car service to pick her up from school when she was 16 so she could visit his home. Mr Davie said he hopes a review, led by BBC’s director of editorial complaints Peter Johnston, will give an “initial report in weeks, not months” and added that “the objective is to be totally transparent”. He also said: “The review will also look at the position regarding any cars used by the BBC at that time – because that was obviously something that, again, in a powerful testimony, was mentioned.” The news comes after the remaining shows of Brand’s Bipolarisation tour were postponed and the Metropolitan Police said it had received a report of an alleged sexual assault in the wake of media allegations. According to Companies House, Brand on Tuesday resigned as a director of both performing arts business One Arm Bandit and filming company Mayfair Film Partnership. Mr Davie has said the broadcasting industry needs to be “very vigilant” following questions being raised about the wider TV industry – which he also said had “faced significant” power imbalance issues in the past. It comes as the Commons Culture, Media and Sport Committee chairwoman Dame Caroline Dinenage has written to the BBC, Channel 4 and TikTok to request further details on what actions they are taking in response to the allegations – and to GB News in relation to their coverage of the claims. The letters also requested updates on the investigation being conducted by Banijay UK, which bought Endemol, the company commissioned by Channel 4 to produce the Big Brother spin-off shows Brand hosted, into his behaviour while he was working on its programmes. Mr Davie also said: “I do think we’re in a different place, over 15 years. When I listened back, frankly, to some of those broadcasts I think, that is just completely unacceptable. What led to that being on air? “I just look at that stuff and I say there is no way I will listen to that, there’s no way I accept it. We have to be clear about that together, that we will not accept that.” Brand has been accused of rape, assault and emotional abuse between 2006 and 2013, when he was at the height of his fame and working for the BBC, Channel 4 and starring in Hollywood films, following a joint investigation by The Times, Sunday Times and Channel 4’s Dispatches. In the documentary, footage was shown of the actor making comments about female BBC staff on his radio show. Brand’s YouTube account, which has 6.6 million subscribers, has been suspended from YouTube’s Partner account “following serious allegations against the creator”, meaning the channel is no longer able to make money from advertising on the platform. In a statement, YouTube said the decision applied to all channels that may be “owned or operated” by Brand, adding: “If a creator’s off-platform behaviour harms our users, employees or ecosystem, we take action to protect the community.” Brand still has a presence on video platform Rumble, where his channel has 1.4 million followers and he hosts a weekly live show at 5pm BST, but there was no new episode on Monday. His most recent video on Rumble is the short clip from Friday denying the allegations and saying he has been “promiscuous” but that all of his relationships have been “consensual”. Dame Caroline has asked TikTok’s director of government relations, Theo Bertram, whether Brand could monetise his posts on the video sharing platform, where he has 2.3 million followers. The committee chairwoman also asked “what the platform is doing to ensure that creators are not able to use the platform to undermine the welfare of victims of inappropriate and potentially illegal behaviour”. Dame Caroline also wrote to GB News chief executive Angelos Frangopoulos over presenter Beverley Turner supporting Brand in a tweet over the weekend and defending him on her show on Monday morning. She acknowledged Turner was challenged on the programme but remained “concerned that having a presenter so clearly supporting an individual who is the subject of intense media coverage, including seeking their appearance on the show, undermines any perception of due impartiality in the broadcasting”. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live BBC removes some Russell Brand content as monetisation suspended on YouTube Google Bard can now link to Gmail and other apps to help with responses How does Russell Brand make money online?
2023-09-20 00:56

Google AI breakthrough represents huge step in finding genes that cause diseases, scientists say
Google says it has made a significant step in identifying disease-causing genes, which could help spot rare genetic disorders. A new model named AlphaMissense is able to confidently classify 89 per cent of all possible “missense” variants in genes, identifying whether they are likely to cause diseases or benign. That compares with just 0.1 per cent of all missense variants that have been confidently classified by human experts. Missense variants happen when a single letter is substituted in the DNA, which in turn leads to proteins with a different amino acid. That small change can have significant effects – Google likened it to the way that changing a letter in one word can change the meaning of the whole sentence. Most of those variants are benign: the average person has more than 9,000 of them. But some of them can be disastrous, leading to rare genetic diseases. The new AlphaMissense looked at existing information about missense variants, and how commonly they are seen in humans and closely-related primates. It looked for those that were rarely seen, classifying them as pathogenic, and from that was able to use that information to analyse other protein sequences – giving not just a verdict on whether they were likely to cause problems, but also how confident it was. Experiments, conducted by humans, which look to find those mutations are expensive and slow: they require people to examine each unique protein and designed separately. Google says that the new system means that researchers can “preview” those results for thousands of proteins at a time, helping them decide where to focus. The company has used its systems to release a vast catalogue of “missense” mutations, so that researchers can learn about what effect they have. In some cases, those variations can lead to conditions such as cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anaemia, or cancer, and understanding them could be key to researchers studying ways to treat or prevent those diseases. It is just the latest health breakthrough from Google’s Deepmind division, which is looking to use artificial intelligence to both identify and treat a variety of conditions. The new system was built on AlphaFold, the breakthrough model that helped unfold proteins, the building blocks of life. The research is described in a new paper, ‘Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with AlphaMissense’, published in the journal Science. The catalogue is being made “freely available to the research community”, Google said, and the company will release the code behind the AI system. Read More BBC removes some Russell Brand content as monetisation suspended on YouTube Google Bard can now link to Gmail and other apps to help with responses Long-form video content is here to stay, says YouTube UK boss
2023-09-20 00:16
