
Persist™ Now Offers Micronized Biochar, Making it Ideal for Precision Fertigation and Liquid Spray Applications
CAMARILLO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 29, 2023--
2023-06-29 19:18

Bidgely Releases Enhanced Analytics Capabilities to Advance DER Grid Planning, EV Load Management and Flex Demand Outcomes
LOS ALTOS, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 29, 2023--
2023-06-29 19:18
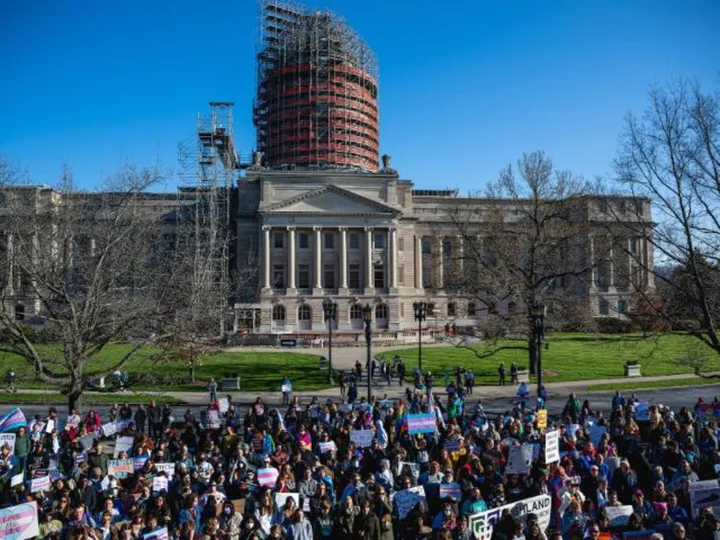

Judge temporarily blocks Kentucky's ban on gender-affirming care for youth
A federal judge on Wednesday temporarily blocked Kentucky Senate Bill 150, which would have prohibited transgender minors from receiving several forms of gender-affirming care. The ruling stops the law from taking effect while other courts hear challenges to the law.
2023-06-29 19:18

Eva Longoria says there were ‘no efforts’ to include Latinos in film when she started career
Eva Longoria feels there were “no efforts” to include Latinos in film when she started her career, and says she ended up feeling like a “poster child” for diversity.
2023-06-29 19:16

Everybody alive today came from one African country, according to study
It’s well known that all humans alive today can be traced back to a common ancestor but a study may have found where that ancestor originates. Researchers at the University of Oxford’s Big Data Institute mapped the entirety of genetic relationships among humans to create the largest human family tree ever. By combining modern and ancient human genomes data from eight different databases, the researchers were able to create a massive family tree. This allowed them to see how a person’s genetic sequence relates to another using the points of the genome. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter “Essentially, we are reconstructing the genomes of our ancestors and using them to form a vast network of relationships,” Lead author Dr Anthony Wilder Wohns said. “We can then estimate when and where these ancestors lived.” Where they lived? Sudan, Africa. Dr Wohns told Reuters, "The very earliest ancestors we identify trace back in time to a geographic location that is in modern Sudan. “These ancestors lived up to and over 1 million years ago—which is much older than current estimates for the age of Homo sapiens—250,000 to 300,000 years ago. So bits of our genome have been inherited from individuals who we wouldn’t recognize as modern humans," Dr Wohns said. Researchers used 3,609 individual genome sequences from 215 populations and samples that ranged from 1,000s to over 100,000 years. By using a new method to compile the data, algorithms were able to predict where common ancestors were in evolutionary trees to explain some patterns of genetic variation. The results were a network of almost 27 million ancestors. “The power of our approach is that it makes very few assumptions about the underlying data and can also include both modern and ancient DNA samples,” Dr Wohns says. Not only does the data help us understand human geology better but the new method could help in other research, like medicine. “The underlying method could have widespread applications in medical research, for instance identifying genetic predictors of disease risk," Dr Wohns added. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-29 18:21

Stephen Hawking theory proved right by man-made black hole
Scientists have managed to simulate their very own black hole in their lab and witnessed how it began to glow. The black hole event horizon was created by a team of physicists from the University of Amsterdam, who used a chain of atoms in a single file to gain further understanding about the behaviour of a black hole. Its creation managed to prove Stephen Hawking's theory from 1974 where the black hole emitted a rare form of radiation. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter They studied the properties of Hawking radiation through the creation of a black hole analog in the lab. According to Science Alert, Hawking radiation happens when "particles born from disturbances in the quantum fluctuations caused by the black hole's break in spacetime." The fact that the radiation exhibits a glow itself is in a strange space anomaly, as the event horizon of a black hole is supposed to be where neither light nor matter is able to get out. We all learn about the strength of a black hole in science class – and how we would all be inevitably sucked in as a result. This is possible due to its density within a certain range of the centre, so even an attempt at travelling beyond light speed (or any velocity in the universe for the matter) would not make this unavoidable. The fake black hole event also caused a rise in temperature that matched theoretical expectations of an equivalent black hole system, - but only when part of the chain extended beyond the event horizon, Science Alert reported. As a result, it is believed perhaps this entanglement of particles that straddle the event horizon plays a big role in generating Hawking radiation. Under simulations that began by mimicking spacetime thought of as "flat," scientists say the radiation was only thermal for a certain range of 'hop amplitudes'. So there may be certain situations where Hawking radiation can emit thermally - and could only be the case where gravity causes a change in the warp of space-time. "This can open a venue for exploring fundamental quantum-mechanical aspects alongside gravity and curved spacetimes in various condensed matter settings," the scientists wrote in their paper published by Physical Review Research. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings
2023-06-29 18:19

Scientists discover gigantic 'structure' under the surface of the Moon
The Moon has been a subject of awe and fascination for millennia, with its shape-shifting powers and enigmatic dark side. And though it’s the one celestial body on which man has taken (small) steps, we still have big leaps to go in understanding its potential and uncovering its secrets. However, one hidden feature of the Moon has been unearthed by scientists and it’s very, very big, and very, very heavy. Buried beneath its South Pole-Aitken basin – one of the largest preserved craters in the Solar System – is a structure which weighs at least 2.18 billion kilogrammes and measures more than 300km (186 miles) in depth and 2,000km (1,243 miles) in length. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter The researchers who made the discovery, all based in the US, posited that the “anomaly” could be made out of metal from the core of an asteroid or oxides from the crystallisation of a magma ocean. "One of the explanations of this extra mass is that the metal from the asteroid that formed this crater is still embedded in the Moon's mantle,” lead author Peter B. James, from Houston’s Baylor University, said in a statement shared with IFLScience. Illustrating just how gigantic this thing is, he went on: "Imagine taking a pile of metal five times larger than the Big Island of Hawaii and burying it underground. That's roughly how much unexpected mass we detected.” The groundbreaking finding was made thanks to NASA’s Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission, which measures changes in the Moon’s gravitational field. Data collected by GRAIL can then be used to study the internal composition of our cratered companion. The South Pole-Aitken Basin has been at the centre of numerous investigations because of just how unique it is. The region offers clues both on the interior composition of our closest satellite and its history, and who knows what other mysteries it holds... Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-29 17:54
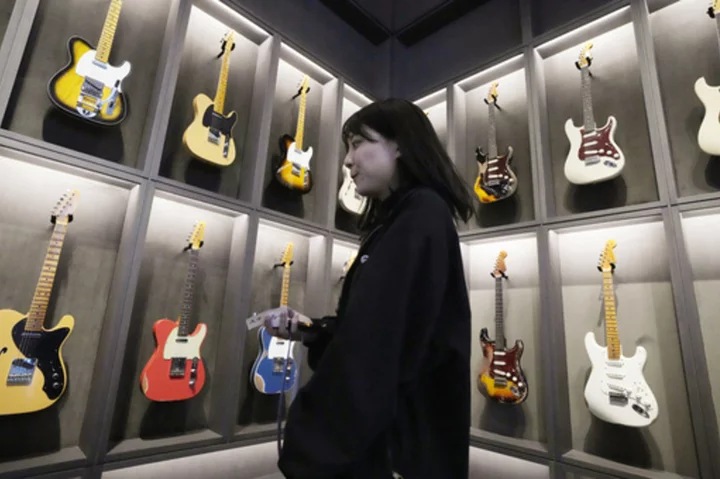

US guitar maker Fender opens flagship store in Tokyo banking on regional growth
Fender, the guitar of choice for some of the world’s biggest stars from Jimi Hendrix to Eric Clapton, is opening what it calls its “first flagship store” in its 77-year history
2023-06-29 17:23

Infant Formula Company Bobbie and Breast Pump Company Elvie Have Joined Forces to Reinvent the Retail Experience for Modern Parents by Normalizing Combo Feeding
SAN FRANCISCO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 29, 2023--
2023-06-29 17:22

Uhuru Joins Top International Companies as Members of Future Investment Initiative (“FII”) Institute
TOKYO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 29, 2023--
2023-06-29 17:17

Music from Teyvat: Minichestra plays Genshin Impact
DUSSELDORF, Germany--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 29, 2023--
2023-06-29 16:27
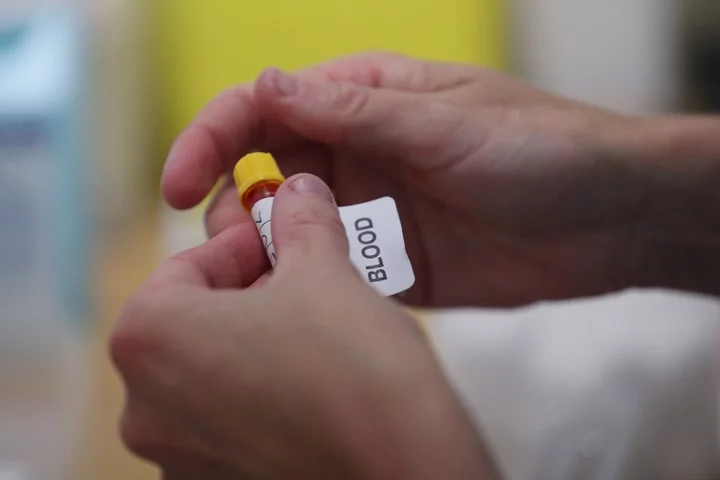
Heart disease digital check-ups for over 40s being rolled out
People over 40 in England will be sent a blood test to carry out at home in a bid to reduce heart disease and obesity. Digital NHS health checks, which will also include an online health questionnaire, will be launched next spring for people aged 40 to 74. Around 15 million people will be eligible, with around one million online checks expected to be carried out over the next four years. Health and Social Care Secretary Steve Barclay said: “Thousands of heart attacks and strokes could be prevented every year through simple health checks, which could save lives and ease pressure on the NHS. “This new digital check-up will mean people can do simple tests and get tailored advice from homes while reducing pressure on GP services.” The home blood test will check cholesterol levels with patients asked to take a blood pressure test at a pharmacy, alongside the online assessment covering details such as weight, height, diet, alcohol intake and exercise levels. Results will be made available online with help available to anyone showing early signs of issues such as diabetes or heart disease, as well as referrals to weight-loss clinics or medication. The online questionnaire will be available via phone, tablet or computer and the Government believes each check will save 20 minutes of NHS time. This could play an important role in helping people live healthier for longer and saving lives in the coming years, while reducing pressure on the NHS Professor Sir Nilesh Silemani Cardiovascular disease is the second biggest killer in England, affecting around 6.4 million people. The Government says the new digital check will help to identify 200,000 people who could benefit from the use of statins, 30,000 cases of hypertension and prevent around 400 heart attacks and strokes over the first four years. Professor Sir Nilesh Samani, medical director at the British Heart Foundation, said: “This initiative will help to reach more people and encourage them to get their blood pressure and cholesterol levels checked so that, where necessary, healthcare professionals can work with them to manage their condition. “This could play an important role in helping people live healthier for longer and saving lives in the coming years, while reducing pressure on the NHS.” Existing NHS health checks for people in the same age group take place face-to-face with a GP and concerns have been expressed that elderly people are not left behind if they struggle with technology. David Baines, vice chair of the Local Government Association, told The Times: “Making more digital health checks available is a useful tool to detect certain illnesses but it should be treated as an addition to, not a replacement for, a physical health check.”
2023-06-29 16:15
