
Toilet invented that is so slippy nothing can leave skid marks
A 3-D-printed toilet has been invented and the surface is so slippery that nothing can leave a mark on it. Cleaning the toilet has to be one of the grimmest household chores, but thanks to new material, you may never have to scrub a loo again. The toilet is the invention of Yike Li at Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, China, who, alongside colleagues, invented a toilet whose surface is so slippery that nothing stains it and uses less water for each flush. The team created a prototype of the toilet around 10 times smaller than a real one. It was made using 3D printing technology, where particles of plastic and hydrophobic sand grains were fused together with lasers. The surface of the toilet was lubricated with a type of silicon oil that also penetrated the surface due to the complex structure of the material. The team tested the toilet with a variety of substances, including honey, yoghurt, muddy water as well as synthetic faeces. They found that none of the substances stuck to the toilet bowl. Amazingly, the toilet was just as slippery after having been rubbed with sandpaper over 1,000 times, which Li believes is due to the oil being able to penetrate the material of the toilet. Li believes the technology would be suited for settings in which a toilet gets a lot of use, such as on modes of transport and in public toilets. He explained: “The reduced flushing volume would result in less wasted water during transportation to the processing facilities, thereby saving transportation costs.” But, before that can happen, Li says the technology needs to be adapted for use on a full-sized toilet and also needs to be cheaper to make. You can see the toilet in action below courtesy of New Scientist. Nothing can stick to this 3D-printed slippery toilet youtu.be Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-22 20:24
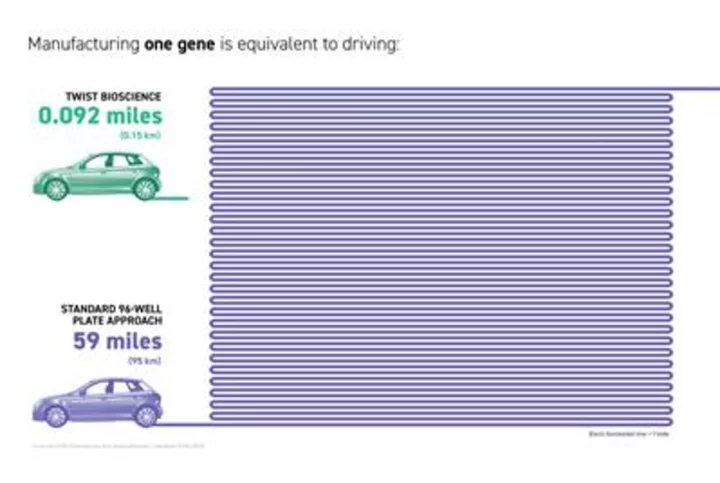
Twist Bioscience Releases 2023 ESG Report and Quantifies Carbon Footprint of Manufacturing a Single Gene
SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 22, 2023--
2023-08-22 20:17

Sprouts Announces 24 School Garden Builds in 24 Hours in 24 Communities
PHOENIX--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 22, 2023--
2023-08-22 19:53

Hong Kong Curbs Japanese Food Imports on Fukushima Discharge
Hong Kong will impose import curbs on seafood to seaweed from parts of Japan in response to a
2023-08-22 19:47

Jack Antonoff inks deals with The 1975's label Dirty Hit and Universal
Jack Antonoff is embarking on a new chapter of his music career with Dirty Hit and a publishing deal with Universal Music Publishing Group.
2023-08-22 19:29

Niman Ranch Names Missouri’s Pastvina Acres 2023 Sustainable Farm of the Year
WESTMINSTER, Colo.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 22, 2023--
2023-08-22 19:22

Coty forecasts downbeat annual profit as goods, labor costs bite
By Juveria Tabassum and Ananya Mariam Rajesh CoverGirl parent Coty forecast annual profit below Wall Street expectations on
2023-08-22 18:55

Prostate screening ‘could save lives’ – the symptoms and risk factors you need to know
There are more than 47,000 men diagnosed with prostate cancer every year in England but new research says using MRI scans can reduce deaths caused by the disease. Current tests usually detect the level of the protein prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the blood, but scientists say this has meant overdiagnosis and overtreatment of low-risk cancer. The Reimagine study, by University College London, University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London, invited 303 men aged between 50 and 75 to have a screening MRI and a PSA test. Of those men, 48 (16%) had an MRI that indicated prostate cancer despite having a median PSA density – 32 of those had lower PSA levels than the current screening benchmark, meaning they would ordinarily not have been referred for investigation. After NHS assessment 29 were diagnosed with cancer that required treatment, and three were diagnosed with low-risk cancer with no need for treatment. Prof Caroline Moore, consultant surgeon at UCLH, chief investigator of the study and NIHR research professor, called the findings “sobering”. She said: “Our results give an early indication that MRI could offer a more reliable method of detecting potentially serious cancers early, with the added benefit that less than 1% of participants were ‘over-diagnosed’ with low-risk disease.” What is prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is the UK’s most common male cancer. It affects the prostate – a walnut-sized gland that sits beneath the bladder and surrounds the urethra in people born with male sex organs. Its main purpose is to help produce semen (the fluid that carries sperm). Prostate cancer can develop when cells in the prostate start to grow in an uncontrolled way. While some prostate cancers grow quickly and spread, others grow too slowly to cause any problems and therefore will never need any treatment. What are the risk factors “Prostate cancer is a disease we tend to see in older age groups (over-50s), but there are exceptions, as with any form of cancer,” said Dr Sanjay Mehta, GP at The London General Practice. According to Prostate Cancer UK black men are at a higher risk – one in four black men will get prostate cancer in their lifetime (compared to one in eight for other men). The risk increases after the age of 45. Family history is important too; your father or brother has had prostate cancer or your mother or sister has had breast cancer, your risk is higher. What are the symptoms? Often there aren’t any signs in the early stages, so be aware of your own risk factors and chat to your doctor if concerned. Prostate Cancer UK have an online risk checker you can use too. Mehta said to watch out for urinary symptoms and changes to how you urinate. “So frequency, where you need to go more often. Hesitancy, where you’re standing over the toilet bowl and a period of time will pass before you’re able to pass urine, and ‘dribbling’, where you’ve finished but find you’re still passing when you walk away. “These are common in older men anyway. But if it’s new for you, and you find you’re having to go more often at night, and you’re having hesitancy or urgency, see your doctor.” Other things to get checked include erectile dysfunction, blood in your urine, and any new and unexplained lower back pain. “Then there are general systemic symptoms, like lethargy, lack of appetite,” added Mehta. “Again, these things often happen anyway, but if it’s a change for you and it’s been happening for a couple of weeks, see your doctor.” How is prostate cancer diagnosed and treated? First, your doctor will chat through your symptoms and history with you. “The next step would involve an examination, including a rectal examination of the prostate,” said Mehta, before referral for further investigations. “I appreciate this can put some men off seeing their doctor but it is a very helpful way of assessing things”. After diagnosis, treatment depends on the stage of the cancer and what’s suitable for each individual, but it may include surgery or radiotherapy. Caught early, prostate cancer is generally very treatable. And even with advanced prostate cancer, treatments have come a long way. Read More Charity boss speaks out over ‘traumatic’ encounter with royal aide Ukraine war’s heaviest fight rages in east - follow live Keep fit to avoid heart rhythm disorder and stroke, study suggests How to give your home a proper summer sort out What you really need to do in autumn to keep your lawn in shape
2023-08-22 18:55

U.S. Department of Labor Registers National Trane Technologies Technician Apprenticeship Program
SWORDS, Ireland--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 22, 2023--
2023-08-22 18:54

Tiffany Young named Moschino's new house ambassador
Tiffany Young has been named as Moschino's new house ambassador.
2023-08-22 18:25

'I had to be good': Archie Madekwe needed to drive perfectly in Gran Turismo
Archie Madekwe was under huge pressure to get the simulated driving scenes right in 'Gran Turismo'.
2023-08-22 17:28

Astronomers are expecting a message from aliens today that is 40 years in the making
Astronomers are hoping to receive a message from aliens after a 40-year wait for a reply comes to an end. On 15 August 1983, a pair of hopeful astronomers at Stanford University beamed a message into space via an antenna. They believe that 22 August 2023 is the earliest time they can expect to receive a reply. The experiment was the brain-child of professors Masaki Morimoto and Hisashi Hirabayashi, who, around 40 years ago, beamed 13 drawings in radio waves to a star named Altair, approximately 16.7 light-years away from Earth. The 13 drawings sent into space by Morimoto and Hirabayashi were designed to tell the story of human evolution and how human beings came to exist on Earth. Drawings depicted how humans evolved from microscopic creatures that eventually moved from water onto land. It also explained our solar system and what DNA is. It was the hope that if there was any intelligent life on planets close to the star, they would interpret the messages and hopefully send a reply. In anticipation of a reply, a team at The University of Hyogo in Japan will monitor for a reply using the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s (JAXA) antenna. Led by Shinya Narusawa, the team will listen for around an hour for signs of unusual radio activity or signals that could suggest a reply. Narusawa explained: “A large number of exoplanets have been detected since the 1990s,” adding, “Altair may have a planet whose environment can sustain life.” Unfortunately, if a reply is received, it will be too late for Morimoto, one of the professors responsible for the original project, after he died in 2010. Dr Hirabayashi, the other pioneer, is currently a professor emeritus at JAXA. It is yet to be seen whether he will see his 40-year experiment gets the conclusion he was hoping for. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-08-22 17:24
