
Scientists have solved a great mystery at the dawn of time itself
Many of us will never get our heads around the fact that scientists can actually look back in time. The power of telescopes enables us to study phenomena that occurred billions of years ago, and even gaze upon the dawn of creation itself. Now, astrophysicists have solved a great mystery at the heart of our universe's birth, when everything was shrouded in a dense fog. In four separate papers published in (or accepted into) The Astrophysical Journal, scientists at MIT, Japan’s Nagoya University, ETH Zurich and the University of Groningen in the Netherlands have shared some stunning insights into the period known as the Epoch of Reionisation. Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Relatively little is known about this era, during which the thick fog engulfing the universe gradually cleared, allowing stars and galaxies to shine. However, fresh observations made using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) are beginning to pull back the curtain on it all. Now, scientists have finally figured out why one billion years after the Big Bang, that dense fog finally dispersed. First things first, what exactly is the Epoch of Reionisation? During the first billion years after the Big Bang, space was filled with a soupy mist of ionised gas which was impenetrable to light. As the gas began to cool, protons and electrons began to combine to form mostly neutral hydrogen atoms and some helium. These clumps of neutral hydrogen are then believed to have started forming stars, grouped into galaxies. This process reionised the gas but, because space had expanded by this point, the newly ionised hydrogen was diffuse enough to allow light to stream through, as Science Alert notes. A few million years later, the universe had become the transparent expanse with which we’re now familiar. To explain, here’s a look at what those four new papers reveal about why space became so much clearer. Paper 1 In the first study, researchers at the University of Groningen revealed that they had discovered crucial evidence of star formation during the Epoch of Reionisation. They found a specific wavelength of hydrogen, called hydrogen alpha, which is formed when a star is born and blasts out huge amounts of ionising ultraviolet radiation. Until now, no one was sure what produced all the ultraviolet light that emerged during the Epoch of Reionisation. But, thanks to their detection of hydrogen alpha, the Groningen team of astronomers that star formation had a “significant role in the process of reionisation”. Paper 2 Another paper, spearheaded by Japanese astrophysicist Daichi Kashino, added galaxies into the mix. According to Kashino and his international team, reionisation happened in “bubbles” around the plethora of newly-formed galaxies. They used JWST data to pinpoint these pockets and measure them precisely, identifying that they had a 2 million light-year radius around the tiny galaxies. Over the next hundred million years, the bubbles grew larger and larger, eventually merging and causing the entire universe to become transparent, according to an article published by NASA. Paper 3 A third group of researchers, led by ETH Zurich astrophysicist Jorryt Matthee, analysed the characteristics of these bubbles and found that the early galaxies they contained were hot, low in metals and dust and very active. He said they were “more chaotic” than those in the nearby universe, adding: "Webb shows they were actively forming stars and must have been shooting off many supernovae. They had quite an adventurous youth!” Paper 4 A fourth paper, led by MIT cosmologist Anna-Christina Eilers, focused its attention on the quasar galaxy at the centre of the JWST observations. This quasar is, according to NASA, an “extremely luminous active supermassive black hole that acts like an enormous flashlight”. Eilers and her team used data from the telescope to confirm that the black hole is the most massive currently known in the early universe, weighing 10 billion times the mass of the Sun. “We still can’t explain how quasars were able to grow so large so early in the history of the universe,” she said. “That’s another puzzle to solve!” Conclusion Well done if you’ve survived to the end – this is all pretty heavy-going. But the key point here is that before the JWST no one knew for sure what caused reionisation. Now, thanks to the mighty golden-eyed telescope, one of the great mysteries behind the birth of creation has finally been solved. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-26 22:53

Introducing Trufacial: An Innovative Skin Perfecting Technology in a Hand-Held Device with Specialized Treatment Tips and Targeted Serums for Professional-Grade Aesthetic Results At Home
PHILADELPHIA--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 26, 2023--
2023-06-26 22:49

French sugar beet pesticide alternative could be five years away
By Sybille de La Hamaide PARIS Research into alternatives to neonicotinoid pesticides, found to be toxic to bees,
2023-06-26 22:26

New Offshore Wind Innovation Hub Announces First Selections for its Accelerator Program
NEW YORK--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 26, 2023--
2023-06-26 21:56
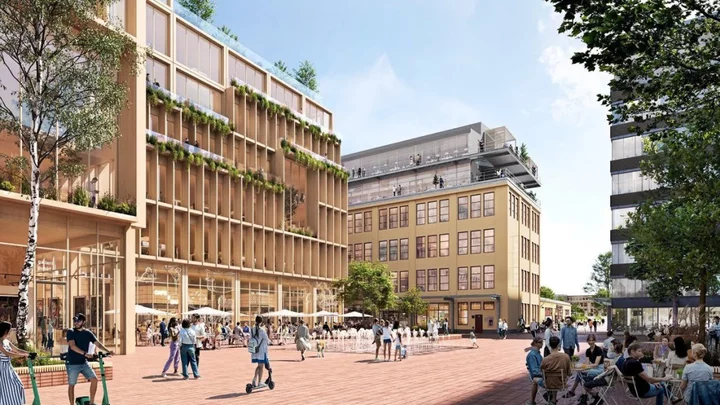

Sweden will have a city made of wood built in the next four years
Sweden is set to have the "world's largest wooden city" with plans for the development in Stockholm. Danish studio Henning Larsen and Swedish architecture firm White Arkitekter are the studios behind the design that will be constructed in the Sickla area of the city. It will use the largest amount of fire-proofed mass timber in a project of this kind with 7,000 office spaces and 2,000 homes, along with shops and restaurants being built. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter This amount of wood will be used to cover the 250,000 square metre development to display the "serenity of a forest" and natural elements will also be part of the buildings. "We sought to create an urban environment infused with the serenity of a forest, resulting in a dense, open space that bears the distinctively minimalistic and functional aesthetic of Scandinavian design," Atrium Ljungberg told Dezeen. "The architects innovatively incorporated natural elements into the structures – for instance, green roofs for better insulation and large windows to let in natural light, embodying our vision of a city that thrives in harmony with nature." The environmental benefits of using this wooden material were noted too as it emits fewer emissions than concrete as well as a reduced climate impact during and after its construction. The project is planned to get underway in 2025, with the first buildings being completed two years later. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-26 21:49

The Equal Parenting Project, in collaboration with Music Football Fatherhood, announces the winners of the Working Dads Employer Awards 2023
LONDON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 26, 2023--
2023-06-26 20:47

Work For Humankind North America: Lenovo Brings its Global Service Project to North America in Partnership with Conservation Group BirdLife International
RALEIGH, N.C.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 26, 2023--
2023-06-26 20:29

Madison Beer has found a new hobby in gaming
Madison Beer feels like she is living a double life after taking up gaming whilst continuing to work on her upcoming album.
2023-06-26 20:16

Astronomers discover a totally new way that stars can die
Astronomers have discovered a new way that stars can die. In a study published in the journal Nature Astronomy, experts have worked out that a minute-long gamma-ray burst of light, which occured in 2019 and evidence a star dying, happened because stars collided within the densely crowded environment near the supermassive black hole at the centre of an ancient galaxy. Normally gamma-ray bursts (GRB) last around two seconds and happen when stars collapse. “For every hundred events that fit into the traditional classification scheme of gamma-ray bursts, there is at least one oddball that throws us for a loop,” said study coauthor Wen-fai Fong, assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Northwestern University’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences, in a statement. “However, it is these oddballs that tell us the most about the spectacular diversity of explosions that the universe is capable of.” Over time, astronomers have observed three main ways that stars can die, depending on their size. Lower mass stars like our sun shed their outer layers as they age, eventually becoming dead white dwarf stars. Sign up to our free Indy100 weekly newsletter Massive stars burn through the fuel-like elements at their core and shatter in explosions called supernovas. Doing so can leave behind dense remnants like neutron stars or result in the creation of black holes. A third form of star death results when neutron stars or black holes begin to orbit one another in a binary system and spiral closer to one another until they collide and explode. But the new observation suggests a fourth type of death. “Our results show that stars can meet their demise in some of the densest regions of the universe, where they can be driven to collide,” said lead study author Andrew Levan, an astrophysics professor at Radboud University in Nijmegen, Netherlands, in a statement. “This is exciting for understanding how stars die and for answering other questions, such as what unexpected sources might create gravitational waves that we could detect on Earth.” “The lack of a supernova accompanying the long GRB 191019A tells us that this burst is not a typical massive star collapse,” said study coauthor Jillian Rastinejad, a doctoral student of astronomy at Northwestern, in a statement. “The location of GRB 191019A, embedded in the nucleus of the host galaxy, teases a predicted but not yet evidenced theory for how gravitational-wave emitting sources might form.” “While this event is the first of its kind to be discovered, it’s possible there are more out there that are hidden by the large amounts of dust close to their galaxies,” said Fong, who is also a member of the Center for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Research in Astrophysics at Northwestern. “Indeed, if this long-duration event came from merging compact objects, it contributes to the growing population of GRBs that defies our traditional classifications.” You learn something new every day. Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the indy100 rankings.
2023-06-26 19:27

Gelesis’ Oral Treatment for Weight Management Showed Real-World Effectiveness in New Data Presented at the American Diabetes Association’s Annual Conference
BOSTON--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 26, 2023--
2023-06-26 19:26
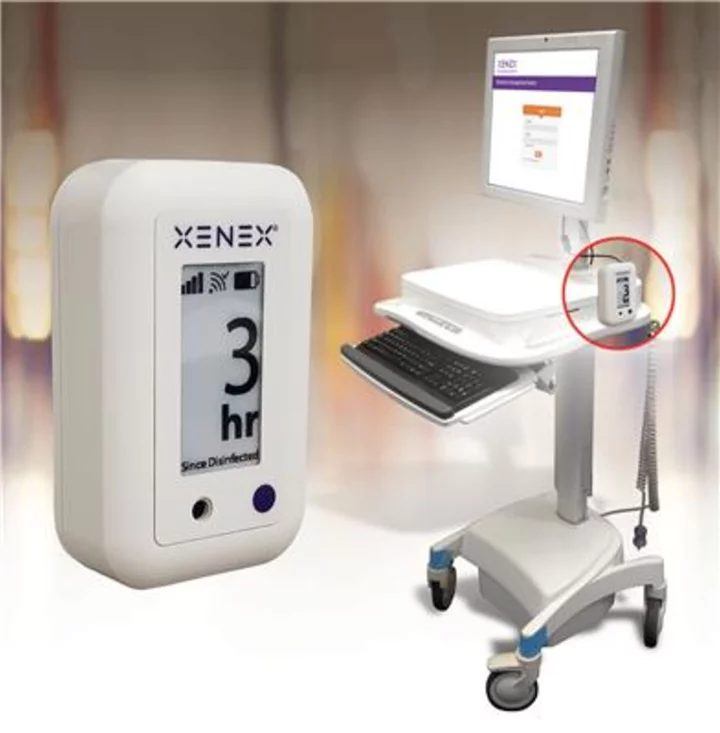
Xenex Announces World’s First Disinfection Tracking System
SAN ANTONIO--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jun 26, 2023--
2023-06-26 19:22

Canada’s Explosive Wildfires Have Damaged a Forest Carbon Offset Project
Canada’s explosive wildfire season has already pumped millions of tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Some of
2023-06-26 18:25
